In aesthetic practice, the question “what is fillmed nctf” usually comes up during protocol design. It also surfaces during procurement reviews and consent updates. Clinics want a clear, operational view. What is it intended to do, how is it positioned, and what should you document?
This guide frames NCTF 135 HA as a skin-quality injectable used within mesotherapy and “skin booster” style plans. The goal here is not to instruct clinical technique. It is to help you evaluate fit, define expectations, and set a compliant workflow.
Key Takeaways
- Clarify category: skin-quality support, not volumization.
- Use labeling: follow IFU, local rules, and trained technique.
- Plan documentation: indications, consent language, outcome tracking.
- Compare thoughtfully: mechanism, injection plane, and patient priorities.
- Operationalize sourcing: verification, traceability, and inventory controls.
What Is Fillmed NCTF and Why Clinics Use It
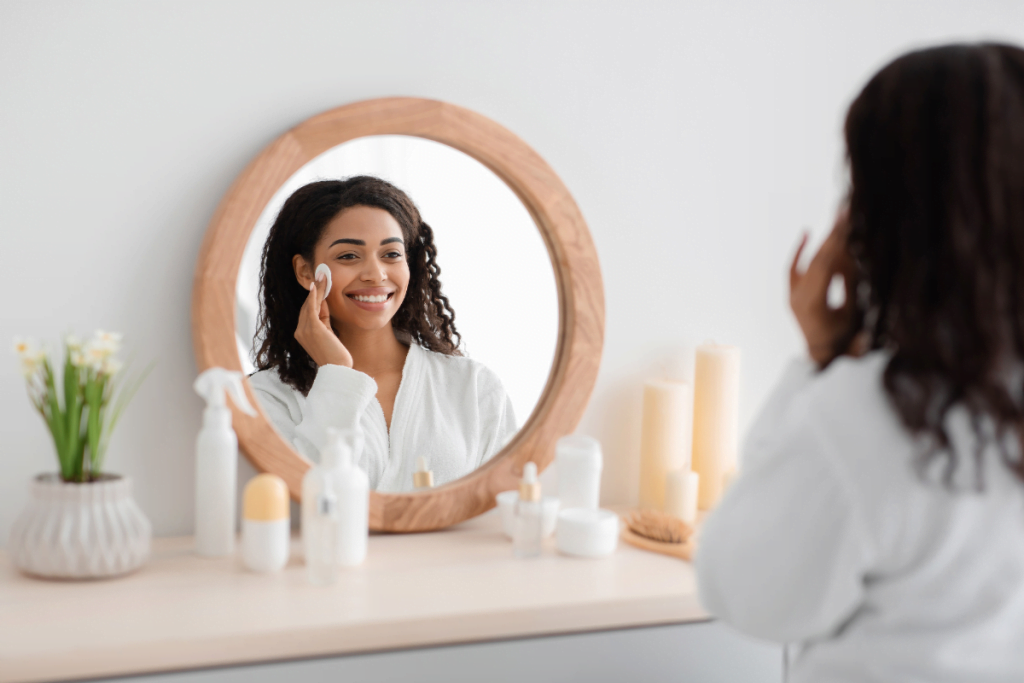
NCTF 135 HA is commonly discussed as a “polyrevitalizing” solution used to improve overall skin quality. In plain language, it is positioned for hydration, radiance, and texture support rather than reshaping or lifting. Many teams group it with skin boosters and mesotherapy injectables. That grouping helps set realistic clinic workflows and patient messaging.
From an operations standpoint, define it by how you intend to use it. Some clinics place it in a prevention and maintenance pathway. Others use it as an adjunct around energy-based treatments or during seasonal “skin reset” plans. Your documentation should reflect that it is a skin-quality approach. It should also distinguish it from volumizing dermal fillers and neuromodulators.
When you review product specifics, start with manufacturer materials and your local regulatory framework. Naming and branding can also be confusing. Some clinicians still reference older “Filorga NCTF” wording. Confirm the exact packaging, labeling, and IFU version used in your facility.
For context on how this product family is discussed in clinic settings, see Fillmed NCTF 135 HA and the broader portfolio overview in Fillmed Filler For Clinics. These can help align internal terminology with your purchasing and clinical teams.
MedWholesaleSupplies supplies only to licensed clinics and healthcare professionals.
NCTF 135 HA Ingredients and Mechanism
Teams evaluating NCTF often ask two practical questions. What is in it, and what is the intended mechanism at a high level? The product name indicates hyaluronic acid (HA), which clinics often describe as a hydrating matrix ingredient. NCTF also gets described as a vitamin and cofactor blend in many educational materials. Specific ingredient lists and presentations can vary by market and labeling, so rely on the IFU for your lot.
At a conservative, clinic-facing level, you can think of these products as supporting the skin’s extracellular environment. HA is widely used in aesthetics to support hydration and viscoelasticity. Added components, when present, are typically framed as supportive “nutrient” cofactors. Clinically, that translates into protocols focused on skin texture, dullness, and fine surface lines. It does not mean structural lifting, deep fold correction, or volumetric replacement.
NCTF meaning in skincare context
In many skincare conversations, “NCTF” functions as shorthand for a multi-ingredient revitalizing solution. Some educational sources expand the acronym as “New Cellular Treatment Factor,” but clinics should treat that as marketing language rather than a clinical endpoint. For operations, the practical meaning is simpler. NCTF indicates a category of mesotherapy-style formulations that aim to support skin quality. Use that framing in staff training, intake notes, and consent language. It helps prevent confusion with crosslinked filler gels and biostimulatory products.
Reading the ingredient list for procurement
For procurement and governance, focus on three checks. First, confirm the exact presentation and intended route per IFU. Second, compare allergens and excipients against your clinic’s standard screening. Third, document the lot and expiry in a way that supports traceability. When staff ask “what is fillmed nctf” in day-to-day operations, your answer should include both clinical category and documentation steps. That reduces inconsistent charting and reduces rework during audits.
For a broader refresher on mesotherapy positioning and language, review Mesotherapy Injections Guide. It can help align how your team describes microinjection-based skin-quality programs.
Indications, Candidate Selection, and Contraindications
In clinic practice, NCTF-style products are usually discussed for skin quality concerns. Common “need states” include dehydration, rough texture, early photoaging (sun-related skin change), or a tired-looking complexion. Documentation should stay descriptive and visual. Record the baseline concern and the intended treatment goal in neutral terms. Avoid implying medical necessity or guaranteed aesthetic change.
Candidate selection is often less about a single diagnosis and more about risk screening. Your intake should include prior filler history, recent procedures, bleeding risk factors, infection risk, and relevant allergies or sensitivities. For under-eye use, clinics typically apply an extra layer of caution. The periorbital region can be more reactive. Swelling and bruising may be more noticeable there, and technique requirements can be more specific.
Why it matters: Clear selection criteria reduces preventable reactions and improves the quality of consent.
Contraindications and precautions should be taken directly from the IFU and your medical director’s protocols. If patients ask for “instant” correction, consider whether a skin booster is the right category. Also separate this conversation from volumizing correction pathways found within your Dermal Fillers Category hub, which typically addresses different goals and risk profiles.
When teams revisit training, a useful phrasing is: “This is a skin-quality plan.” It sets expectations for gradual change and maintenance. It also keeps messaging aligned when patients bring in social-media “before and after” images that may not match your outcomes documentation standards.
Protocol Planning: Intervals, Combination Care, Documentation
Most clinics treat skin-quality injectables as a program rather than a single event. That does not mean you should standardize a one-size schedule. Instead, document a protocol concept: an initial series, a reassessment point, and a maintenance discussion. Exact timing, session counts, and injection details must follow IFU, training, and clinician judgment. Your operational aim is consistency in how plans are proposed and tracked.
During protocol planning, explicitly define where this fits among other modalities. Some practices combine skin-quality injections with topical regimens, peels, or device-based treatments. Others keep them separate to simplify attribution of results and adverse event tracking. If you use adjunctive modalities, document sequence and spacing rules in your SOPs. Keep the chart clear on what happened when.
MedWholesaleSupplies sources brand-name medical products through vetted distribution channels.
Documenting before-and-after responsibly
“Before and after” is often the only language patients recognize. In a clinic chart, you need a more controlled approach. Use standardized photography, consistent lighting, and a reproducible pose set. Record which areas were treated (face, neck, or décolletage), and note concurrent treatments. Add a brief patient-reported outcome statement, such as hydration or texture perception, without leading questions. If you track satisfaction, use the same scale each time. This structure helps you interpret change without overclaiming causality.
If you want a comparator for skin hydration-focused approaches, review How Restylane Skinboosters Vital and the related product context in Restylane Skinboosters Vital. These references can help staff distinguish “skin booster” language from traditional filler terminology.
How to compare options: When deciding between NCTF-style mesotherapy, HA skin boosters, PRP (platelet-rich plasma), or other injectables, focus on:
- Primary goal: hydration, glow, or structure.
- Mechanism: HA matrix vs bioactive approach.
- Procedure style: microinjection vs cannula placement.
- Downtime tolerance: bruising and swelling expectations.
- Documentation: photos, adverse events, re-treatment logic.
For an overview of another widely discussed hydration approach, see Profhilo Injections Overview and the related reference product Profhilo Structura. Use these as discussion aids, not as a substitute for IFUs.
Safety, Injection Technique Concepts, and Aftercare
Risk management starts with defining the category correctly. Skin-quality injectables are still injections. They can trigger bruising, swelling, tenderness, erythema (surface redness), and transient lumpiness. They can also complicate interpretation when patients receive multiple treatments in a short window. Your protocol should include a standard adverse event log and a consistent follow-up touchpoint, even if remote.
Technique detail belongs in hands-on training and the manufacturer’s IFU. Still, it helps to define technique concepts for staff alignment. These treatments are often described as superficial placement through multiple small injection points. Some clinics may also consider microneedling-adjacent delivery tools, depending on local scope and device labeling. If you use specialty micro-needles, ensure the team understands device compatibility, sterile field requirements, and sharps handling.
For teams that use micro-needle style accessories for intradermal delivery, see Fillmed Nanosoft Microneedles as a reference point for the type of tool that may appear in training discussions. Always align any technique choice with clinician training and device labeling.
Aftercare instructions should be clear and conservative. Use standardized language about expected short-term reactions and basic hygiene. Avoid over-prescriptive steps that could be interpreted as individualized medical advice. Also document what you told the patient and what materials you provided. That matters if patients later report a reaction and your team needs to triage consistently.
Common pitfalls to avoid:
- Vague charting: missing sites and product identifiers.
- Overpromising: language that implies guaranteed transformation.
- Stacking treatments: unclear timing between procedures.
- Inconsistent photos: lighting changes hide or exaggerate effects.
- Weak escalation plan: no standard response to swelling concerns.
When staff ask again “what is fillmed nctf,” include safety language in the answer. A short, consistent script reduces misunderstandings and supports more uniform consent.
Operational Fit for Clinics: Sourcing and Workflow
Operational fit is often the deciding factor for adding any injectable. Your team needs reliable product verification, consistent documentation, and predictable inventory controls. Start by defining who owns each step: ordering, receiving, storage, and lot capture in the EMR. Then test the workflow with a small cohort of clinicians before broader rollout.
MedWholesaleSupplies distributes authentic, brand-name medical products for professional use.
Clinic workflow snapshot
A simple workflow reduces variation across shifts. Verify the clinic account and licensure requirements with your supplier. Document product name, lot, and expiry at receiving and at point of use. Store per labeling, and limit access to trained staff. Dispense or administer under clinician oversight according to your internal governance. Record outcomes and adverse events in a consistent format. Finally, reconcile inventory regularly to reduce documentation gaps. If you operate within US distribution networks, confirm that your receiving process matches your internal compliance policies.
Quick tip: Keep one shared “product facts” sheet tied to the IFU version.
It can also help to map where NCTF-style products sit alongside other “skin booster” lines. Clinics that already carry regenerative-positioned products may want a single education framework for staff. For related reading on another skin-renewal category, see Rejuran Skin Booster. Use it to standardize how you compare categories and set expectations.
Close the loop with a brief quarterly review. Look at photo consistency, consent completeness, and the adverse event log. That is often where small documentation issues surface. It is also where you can decide whether “what is fillmed nctf” is still being answered consistently across your team.
Authoritative Sources
Regulatory status and permitted claims vary by jurisdiction. Avoid relying on secondary summaries or social media posts for compliance decisions. Instead, confirm the product’s labeling, IFU, and local classification. If you operate across multiple sites, standardize how you store these documents and how staff access them.
When patients or colleagues ask whether a product is “FDA approved” or “CE marked,” clarify terminology. In the US, FDA pathways vary by product type and intended use. In the EU, CE marking is tied to conformity assessment and device rules. Your compliance lead should verify the exact status for the specific product presentation you use.
- FDA overview of dermal fillers and risks
- European Commission explanation of CE marking
- American Academy of Dermatology filler safety overview
Further reading within your team can include internal SOPs, device labeling, and your complication management plan. Keep language consistent across intake, consent, and post-care instructions.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.