In aesthetic practices, hyaluronic acid (HA) dermal fillers sit at the intersection of technique, safety, and supply chain discipline. Revanesse filler is often evaluated alongside other HA gels when you are standardizing products across indications, training, and inventory. For clinics, “precision” usually means repeatable handling, predictable swelling patterns, and clear documentation pathways.
This guide is written for licensed healthcare professionals and clinic teams. It focuses on how to evaluate an HA filler family for facial features, with special attention to lips, workflow, and risk controls. It avoids dosing guidance and product claims that should be taken from the official labeling.
If you want a broader starting point on HA gels, you can review the Hyaluronic Acid Fillers hub and the general Dermal Fillers category for portfolio context.
Key Takeaways
- Match filler choice to anatomy, plan, and handling preferences.
- Set lip expectations around swelling, asymmetry, and staged refinement.
- Standardize contraindication screening and complication readiness protocols.
- Build a repeatable receiving-to-record workflow for traceability.
Where Revanesse filler Fits in an HA Filler Portfolio
Practices rarely evaluate one gel in isolation. Most teams compare product families based on intended use by area, injector comfort, and how easily the clinic can maintain consistent stock. If you are building protocols for multiple providers, a key question is whether the product line supports a “limited formulary” approach. That approach can reduce variability in technique training, consent language, and follow-up scheduling.
When clinicians look at online chatter such as revanesse filler reviews, the most useful signals tend to be operational rather than promotional. For example, does the review describe injection feel, immediate tissue response, or how follow-up visits were managed? It helps to cross-check those impressions against sources you can audit, including labeling, manufacturer education, and internal complication logs.
MedWholesaleSupplies is structured to serve verified licensed healthcare accounts.
For an overview of common comparisons seen in clinics, the article Revanesse Vs Juvederm is a useful orientation. For a wider view of product classes, see Types Of Dermal Fillers.
Formulation Basics That Affect Handling and Planning
Most products discussed in this category are HA gels, meaning the base polymer is hyaluronic acid. In plain language, HA is a sugar-based molecule found in human tissues that binds water. In fillers, the HA is processed into a gel designed to persist longer than native HA. Product families can differ in crosslinking approach, HA concentration, particle structure, and whether a local anesthetic is included.
Those formulation choices show up clinically as handling differences. You may notice variations in extrusion force, how the gel integrates during massage, and how quickly visible edema (swelling) settles. Even when two products are both “HA fillers,” they can behave differently in superficial versus deeper planes. That is why portfolio decisions usually combine clinical preference with a conservative approach to training and indication boundaries.
Inventory in this category is typically sourced as authentic, brand-name medical product.
Quick Definitions (Clinic-Facing)
- Hyaluronic acid (HA): A water-binding biopolymer used to form filler gels.
- Crosslinking: Chemical linking that slows HA breakdown in tissues.
- Rheology: How a gel flows and resists deformation under force.
- Integration: How smoothly a gel blends with surrounding tissue.
- Lidocaine: A local anesthetic sometimes included for comfort.
If you are building a “comfort-first” standard, confirm which presentations include anesthetic and how that changes your counseling and documentation. For background on anesthetic inclusion, see Lidocaine In Dermal Fillers. When you review any Revanesse hyaluronic acid filler option, treat the instructions for use as the governing reference for indications, contraindications, and handling.
Clinics often keep representative product pages bookmarked for quick access to packaging details and labeling references. Examples include Revanesse Kiss Lido for lip-focused workflows and Revanesse Contour With Lidocaine when reviewing contouring-oriented inventory. Use these as operational references, not substitutes for official product information.
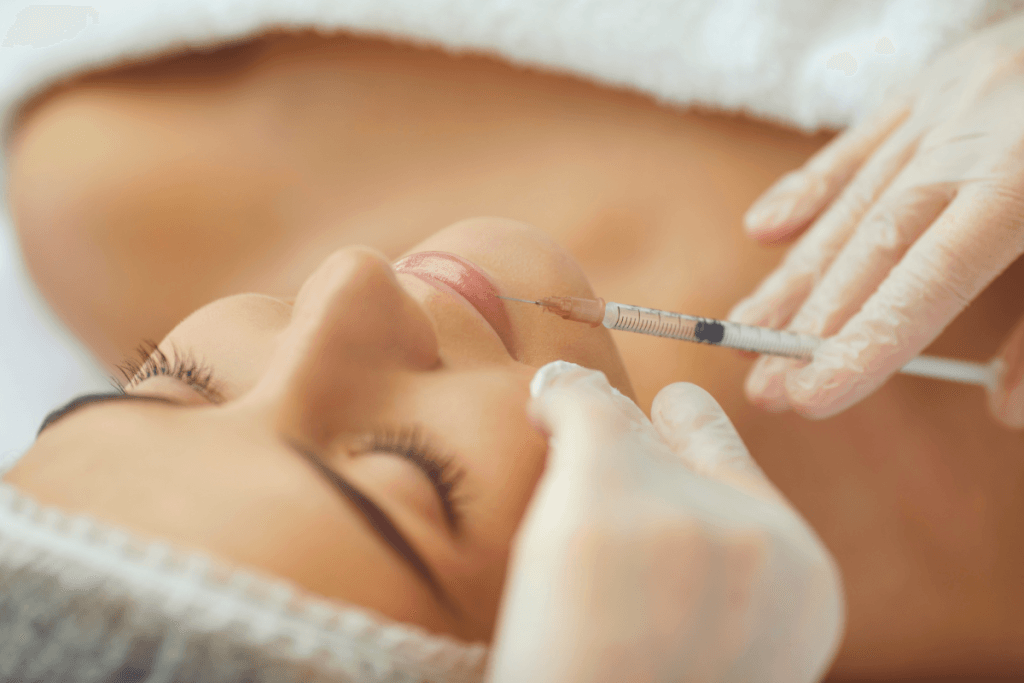
Lip Augmentation Planning: Anatomy, Expectations, and Follow-Up
Lips create a unique planning challenge because small volume changes can look large. Patients also focus on symmetry, border definition, and feel. In clinic terms, this is where protocol discipline matters. Your intake and consent language should cover short-term changes that can be normal after injection, especially swelling and bruising that can obscure the early result.
When patients ask about “revanesse lips” outcomes, it helps to translate the request into objective goals. Are they asking for more vermilion show, better cupid’s bow definition, or improved perioral hydration lines? You can then select technique and product based on tissue quality and risk tolerance, rather than on trend-driven photos.
Set Expectations Around Swelling and “Before and After” Timing
Online searches like revanesse filler before and after can raise unrealistic expectations about day-one results. From an operations standpoint, you can reduce post-visit messages by standardizing your counseling script. Explain that early post-injection appearance reflects both gel placement and tissue response. The tissue response includes edema and sometimes focal firmness that changes over time. A simple, consistent message helps patients interpret early asymmetry and avoid unnecessary touch-ups.
Many teams also document a Revanesse swelling timeline internally, even if the precise pattern varies by patient. In plain language, you are describing typical swelling stages: immediate fullness, then several days of variable edema, then gradual settling. Your documentation should note that timelines vary and that patients should follow your clinic’s written aftercare handout. Keep your aftercare aligned with the label and your medical director’s policy.
For broader counseling language and duration framing, link your staff to How Long Do Lip Fillers Last and Types Of Lip Fillers. These resources help front-desk and nursing teams answer common non-clinical questions without improvising.
Revanesse aftercare should be communicated in a way that is consistent, documented, and easy to repeat. If your clinic uses templated notes, include fields for injection site, product lot identifiers, and the aftercare version provided. That creates continuity if a different clinician handles follow-up.
Adverse Effects, Contraindications, and Safety Readiness
Any injectable filler program should treat safety as a system, not an individual skill. The most common short-term reactions across HA gels include injection-site swelling, bruising, tenderness, and transient lumps. These are typically self-limited, but they drive most after-hours calls. Your clinic can reduce friction by using a consistent triage script that differentiates expected post-procedure changes from red-flag symptoms.
Revanesse side effects should be discussed using product-specific labeling language, then reinforced with plain-language synonyms. For example, “erythema (skin redness)” and “edema (swelling)” are clearer when both terms are used once. It is also reasonable to align on a shared definition of “normal post-injection firmness” so that staff do not over-escalate benign findings.
Contraindication Screening Should Be Standardized
Revanesse contraindications, like contraindications for other HA fillers, need a consistent screening process. Policies vary by clinic and jurisdiction, but your workflow should make it hard to skip required questions. Screen for known hypersensitivity risks per labeling, relevant infection at or near the intended injection site, and other exclusion criteria stated by the manufacturer. Document the screening result in a structured way, not only in free text. This improves auditability and supports consistent care across providers.
Why it matters: A standardized screen reduces avoidable variation across injectors and locations.
Revanesse safety profile discussions should stay tied to the official product information and your complication readiness plan. Clinics should also maintain internal training on recognition and escalation pathways for rare but serious complications that can occur with any dermal filler injection. Avoid relying on informal sources, even if patients bring them up during consults.
Clinic Operations: Verification, Receiving, and Documentation
For practice managers, filler success also depends on sourcing and inventory controls. Your process should confirm that products are obtained through legitimate channels and that you can document what was administered, when, and by whom. That includes storing packaging details and lot identifiers per your policy and local requirements.
MedWholesaleSupplies notes products are sourced through vetted distribution channels.
If you are centralizing procurement, consider limiting the number of SKUs on shelf. A smaller set can simplify training, reduce picking errors, and make par-level management easier. Category hubs can help you map your formulary. Start with Dermal Fillers Product Category and then narrow to specific brands and presentations as your protocols mature.
Documentation and Receiving Checklist
- License verification step: Confirm account credentials per supplier policy.
- Shipment inspection: Check packaging integrity on receipt.
- Label match: Verify product name and presentation.
- Lot capture: Record identifiers in inventory system.
- Expiry review: Confirm dates before shelving.
- Storage per IFU: Follow labeled temperature and light guidance.
- Access control: Limit handling to trained staff.
Quick tip: Use a single intake form for all HA filler deliveries.
For multi-site practices, define where products are staged and who can transfer them. If you use shipped from the US inventory flows, document the internal handoff point so chain-of-custody is clear. Keep your procedures generic enough to apply across brands, and always defer to each product’s IFU for storage conditions and in-clinic handling limits.
Clinic Workflow Snapshot (High Level)
- Verify: Confirm account and authorized receivers.
- Document: Capture product identifiers on receipt.
- Stock: Store according to labeled requirements.
- Prep: Stage for scheduled sessions with double-checks.
- Administer: Record product and site in the chart.
- Monitor: Use a consistent post-visit triage pathway.
- Reconcile: Audit inventory against procedure logs.
Comparing HA Fillers Without Over-Promising Longevity
Clinics frequently need to answer “how long does juvederm filler last” and similar questions like how long does restylane filler last, how long does belotero filler last, or how long does rha filler last. A safe, accurate approach is to explain that duration depends on product, placement depth, area mobility, patient metabolism, and technique. Then point back to labeling and your clinic’s typical follow-up schedule, rather than giving a fixed timeframe.
When comparing families, focus on decision factors you can defend in documentation. These include indicated treatment areas, lidocaine inclusion, handling characteristics, and your team’s training standardization. This is also where online threads such as revanesse vs juvederm for lips reddit can be actively unhelpful. They may mix products, indications, and injection techniques, and they rarely reflect controlled documentation.
If your clinic wants a structured comparison workflow, pair educational articles with a small set of reference SKUs. For example, you might review Restylane Vs Juvederm, then cross-check labeling details on representative pages like Juvederm Volbella With Lidocaine, Restylane 1 mL, Belotero Balance, and Teosyal RHA. For lip-focused planning, the technique-oriented overview Art And Science Of Lip Augmentation can help align provider language.
Some clinics also compare Revanesse vs Juvederm longevity as part of formulary planning. Treat that as a documentation exercise rather than a marketing claim. Define what “longevity” means in your practice, how you measure it, and how follow-ups are scheduled. If you cannot measure it consistently, avoid promising it.
Authoritative Sources
Use these references to anchor counseling language and clinic policies to widely accepted standards. Always defer to the specific product labeling for indications and contraindications.
- FDA overview on dermal fillers
- ASDS patient and clinician resource on dermal fillers
- American Academy of Dermatology on soft tissue fillers
Further reading on site can include your internal protocol set and a short list of product IFUs that your team reviews annually.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.