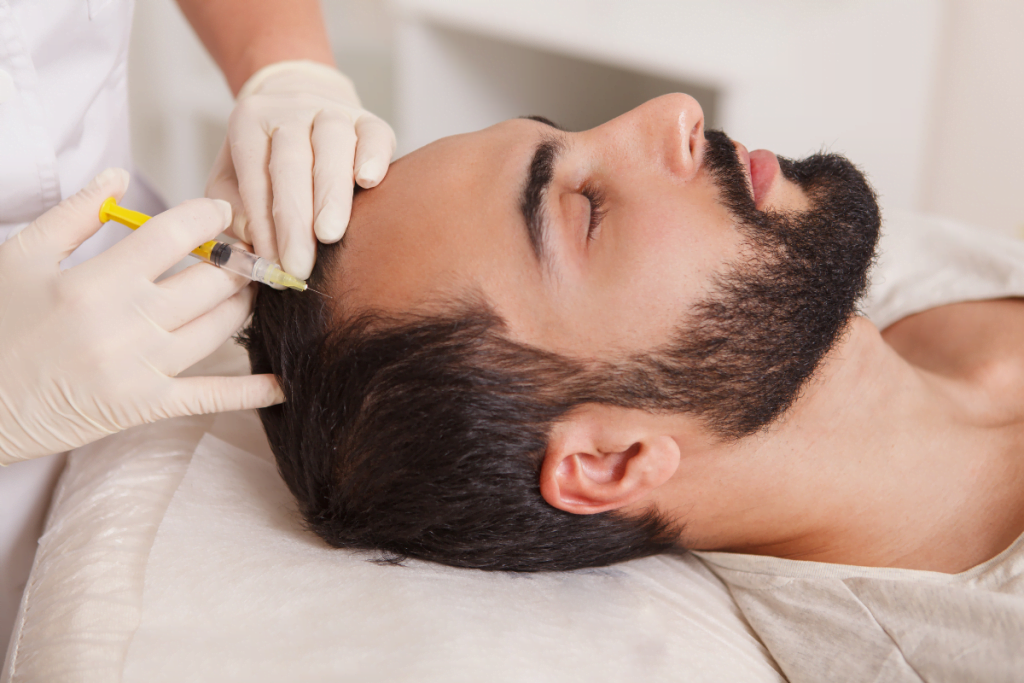
Patients with thinning hair often ask about new “filler” options. The term shows up in clinic consults, social media, and OTC marketing. For healthcare teams, the first step is defining scope and setting expectations. When staff can answer what are hair fillers, they can also screen misinformation and route patients to appropriate evaluation.
This guide frames hair fillers as a category label, not a single standardized therapy. It outlines common ingredient families, delivery pathways, safety planning, and operational steps. It is written for licensed clinics, medical spas, and procurement teams building a consistent process.
Key Takeaways
- Define the category: “Hair filler” can mean injectables or cosmetics.
- Standardize intake: Document diagnosis, photos, and baseline hair metrics.
- Plan for safety: Treat scalp injections like any procedure-based service.
- Compare objectively: Position against PRP, transplant, and minoxidil carefully.
- Operationalize sourcing: Verify lots, documentation, and storage requirements.
What Are Hair Fillers in Clinical Practice?
In practice, “hair filler” is an umbrella term for interventions marketed to improve the look of thinning hair or scalp quality. Clinics typically encounter it in two forms. The first is injectable scalp products used in mesotherapy-style protocols. The second is topical “hair filler” branding on shampoos and conditioners, which is cosmetic by definition.
Because the term is not a single regulated class, your intake should start with clarification. Ask what the patient believes they are getting, where they heard it, and whether they mean an injection or a topical product. Then anchor the visit to the underlying condition. A structured hair-loss evaluation and consistent education improve triage and reduce mismatched expectations. For browsing related clinic-use items and hair-loss supply groupings, teams often start with the Hair Loss Category and the Hair Loss Articles Hub. For patient context that intersects with early-onset shedding, see Hair Loss In Young Adults.
Where named products fit (as examples)
Clinics may see brand-specific requests, including dr cyj hair filler. Treat brand interest as a starting point for education, not a substitute for diagnosis. If you stock or evaluate a specific injectable, keep your counseling anchored to its labeling, intended professional use, and your local scope-of-practice rules. For internal background reading, the site’s overview Dr. CYJ Hair Filler Overview can support staff orientation. When a product is discussed operationally, reference the exact item record, such as Dr. CYJ Hair Filler 1 mL, to reduce mix-ups in ordering and documentation.
MedWholesaleSupplies supports licensed clinics and healthcare professionals only.
How Do Hair Fillers Work? Ingredients and Mechanisms
Most injectable “filler” positioning for hair relies on the idea of improving scalp environment rather than “adding hair.” Mechanisms are often described in terms of hydration, conditioning of the scalp, or support of follicular function. At a high level, products in this space may include peptides (short amino-acid chains), hyaluronic acid (a water-binding polysaccharide), amino acids, vitamins, nucleotides, or other skin-conditioning components.
When teams are asked what are hair fillers, it helps to use plain language: many are scalp-injected “skin boosters” adapted for hair-bearing areas, while others are cosmetics that coat or smooth hair fiber. The evidence base varies widely by product, study design, and endpoint. Build internal talking points that separate plausible biologic rationale from proven clinical outcomes, and update them as labeling or published data changes.
Why it matters: Clear mechanism language prevents staff from implying guaranteed regrowth.
Common ingredient families you will hear about
Patients and staff may use shorthand like “peptide hair filler” or “scalp hyaluronic acid hair filler.” Those phrases usually signal ingredient classes, not a diagnosis or a single standardized protocol. In consults, translate marketing terms into categories you can document: peptides, humectants (water-binding agents), and supportive nutrients. You may also see “keratin hair filler” language, which is more common in cosmetic fiber-smoothing claims than in medical injection workflows. Keep a shared glossary in your clinic SOP so front-desk and clinical staff use the same definitions. If you offer adjunct procedures, link ingredient counseling to your broader service education, such as Benefits Of Mesotherapy.
Administration Pathways: Injectable vs Topical “Hair Filler”
The same phrase can describe very different patient experiences. Injectable approaches are procedure-based, with consent, aseptic technique, and post-procedure monitoring. Topical “hair filler” products, including what is hair filler shampoo or “filler” conditioners, are cosmetic routines. They may improve hair feel, reduce breakage appearance, or add temporary smoothness, but they do not function like an in-clinic injection service.
In patient conversations, you can normalize the confusion. Many people read garnier fructis hair filler reviews or ask about garnier hair filler conditioner and assume it is comparable to a hair filler injection. A simple explanation helps: cosmetics act on hair shafts, while clinic procedures address scalp or follicle-adjacent factors. When your team answers what are hair fillers, include a brief “route of administration” statement and document what was discussed.
| Pathway | Typical setting | What it targets | Clinic documentation focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injectable scalp products | Clinic procedure room | Scalp skin environment | Consent, lot numbers, aftercare notes |
| Topical “filler” shampoo/conditioner | At-home cosmetic routine | Hair fiber feel and appearance | Education notes, compatibility with treatments |
| Camouflage (fibers, styling) | At-home or salon | Visual density | Expectation-setting, photo standardization |
For clinics that provide needle-based scalp services, staff training often overlaps with broader mesotherapy education. A useful internal refresher is Mesotherapy For Hair. If you evaluate peptide-focused inventory, keep product records easy to find, such as BCN Capillum Peptides.
Safety and Adverse Event Planning
Safety planning should be the center of any injection-based hair service. Hair filler treatment side effects can include short-term local reactions such as tenderness, erythema (skin redness), swelling, bruising, or pruritus (itching). As with any injection, infection risk exists when aseptic technique breaks down. Some patients will also report transient headache or scalp tightness, which should be documented and trended.
Build an adverse event pathway that matches your facility type and local regulations. Standardize pre-procedure screening, allergy history capture, anticoagulant and supplement review per your clinic policy, and post-procedure instructions. Staff should know what to escalate, how to document, and when to refer back to the prescriber or supervising clinician. If your intake includes hair filler injection before and after photos, standardize lighting, distance, and part-line placement to reduce false “change” signals.
- Common pitfalls: Vague consent language that omits off-label context.
- Common pitfalls: Missing lot numbers and expiration dates in the chart.
- Common pitfalls: Non-standard photos that undermine follow-up comparisons.
- Common pitfalls: Overstating timelines for visible density changes.
Inventory is authentic, brand-name medical product stock.
Comparing Options: Hair Fillers vs PRP, Transplant, Minoxidil
Clinics benefit from a consistent comparison framework, because patients rarely consider “hair fillers” in isolation. Many are also evaluating hair fillers vs prp, hair fillers vs hair transplant, or hair filler vs minoxidil. Your role is not to pick for the patient in a vacuum. It is to explain what each approach is designed to do, what monitoring looks like, and what tradeoffs exist.
When asked what are hair fillers, you can position them as one supportive modality that may fit alongside diagnosis-based care. PRP (platelet-rich plasma) is an autologous procedure, with variability by kit, processing, and protocol. Transplant is surgical redistribution and has candidacy constraints. Minoxidil is a drug option with labeled use patterns that require clinician oversight. If your team needs a starting point for internal reading on PRP workflows, see PRP Therapy With Regenlab.
How to compare (clinic-facing decision factors)
Use a short set of factors that stay stable across consults. First, diagnosis fit: androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, scarring alopecias, and traction alopecia have different pathways. Second, invasiveness and monitoring: surgery and injectables require more procedure governance than topicals. Third, evidence quality: look for controlled outcomes that match your endpoint, not just testimonials. Fourth, maintenance burden: include visit cadence, at-home steps, and photography follow-up. This keeps counseling consistent, even when hair filler injection reviews or “before and after” posts raise expectations.
Clinic Operations: Workflow, Sourcing, and Records
Operational readiness determines whether a service runs safely and consistently. Define who can counsel, who can administer, and who can document. Then map each step from patient intake to follow-up photography. If you support multiple brands or formulations, add a naming convention in your EHR to prevent mix-ups between similarly described products.
For procurement teams, align sourcing and receiving with your broader injectable governance. Confirm storage needs from official materials, track lot and expiration, and document chain-of-custody steps that matter for audits. If your clinic depends on US distribution for predictable replenishment, build reorder thresholds that reflect actual utilization rather than social media demand spikes. Examples of inventory records clinics may evaluate include Nucleofill Hair and Croma Philart Hair.
Quick tip: Keep one standardized photo protocol in every treatment room.
- Verify: Confirm patient identity, diagnosis workup status, and contraindication screening per policy.
- Document: Consent, baseline photos, and planned follow-up checkpoints.
- Receive: Record lot, expiration, and packaging condition on arrival.
- Store: Follow labeled storage guidance and separate look-alike items.
- Administer: Use aseptic technique and procedure-room checklists.
- Record: Capture product identifiers, site notes, and aftercare instructions given.
- Clinic checklist: Consent template includes realistic outcome language.
- Clinic checklist: Lot/expiry fields are required in charting.
- Clinic checklist: Aftercare handout matches your procedure SOP.
- Clinic checklist: Photo consent stored and retrievable.
- Clinic checklist: Staff script addresses topical vs injectable confusion.
- Clinic checklist: Adverse-event log reviewed on a set cadence.
When staff field “what are hair fillers” during scheduling, route the question to a scripted intake flow. That script should note whether the caller means a topical product, a procedure, or a brand request. It should also set expectations that candidacy depends on clinical assessment and local scope-of-practice requirements.
Sourcing runs through vetted distributor partners.
Authoritative Sources
Because the term “hair filler” is used inconsistently, anchor your internal education to organizations that publish conservative guidance on hair loss evaluation and procedure safety. This is especially important when patients bring hair filler before and after images that lack lighting controls or disclose little about baseline diagnosis.
When your team revisits what are hair fillers, use these sources to reinforce diagnosis-first counseling and injection safety fundamentals:
- American Academy of Dermatology: Hair loss overview
- MedlinePlus: Hair loss basics
- FDA: Dermal filler device information and safety
If you want deeper internal reading, keep a short library for staff refreshers, and update it when your service mix changes. The goal is consistent counseling, consistent documentation, and a clear escalation path.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.