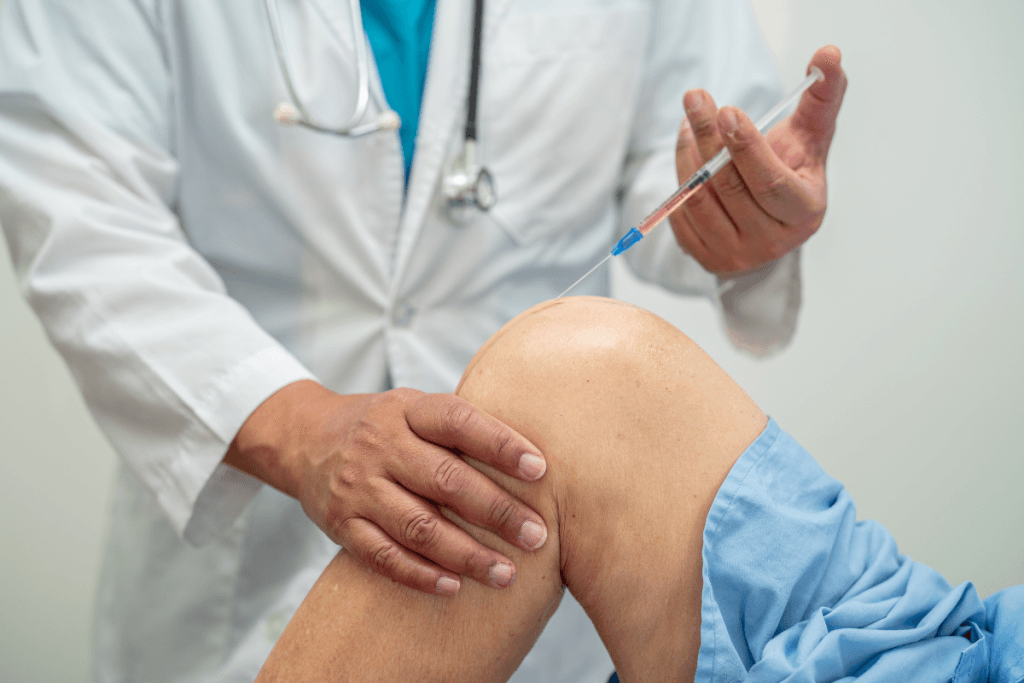
Knee osteoarthritis (knee OA) remains a high-volume driver of pain visits. Many clinics use injections to bridge patients to rehab, delay surgery, or manage flares. In that landscape, cingal 4ml often comes up as a single-visit option that pairs a viscosupplement (hyaluronic acid “gel”) with a corticosteroid. For procurement and clinical leaders, the practical questions are predictable: where it fits among knee osteoarthritis injection options, what the evidence can reasonably support, and what your team must document and monitor.
This guide is written for licensed practices. It focuses on workflow, safety framing, and comparison points. It does not provide dosing or prescribing instructions. Always follow local labeling, credentialing rules, and your own protocols.
Orthopedic Injectables are often managed across departments. That makes standardization important, especially for single-injection viscosupplementation pathways.
Key Takeaways
- Confirm regulatory status and labeling in your jurisdiction.
- Document indication, consent, lot data, and follow-up plan.
- Screen for infection risk and steroid-related precautions.
- Align storage, handling, and inventory controls with the IFU.
- Compare options using decision factors, not marketing claims.
cingal 4ml in Knee OA Pathways: Overview and Positioning
Cingal is commonly described as a combination intra-articular injection for knee OA. It pairs hyaluronic acid (a lubricating, shock-absorbing polymer) with triamcinolone (a corticosteroid). The intent is to address pain and inflammation early while also supporting joint lubrication over time. Clinics often evaluate it alongside other “gel injections,” which are discussed in Types Of Gel Injections and broader background pieces like Understanding Rooster Comb Injections.
From an operations view, treat it as a distinct pathway, not “just another HA.” It involves steroid-related screening, counseling, and documentation that may differ from a hyaluronic acid–only product. Regulatory classification also matters. In some countries, hyaluronic acid injections are regulated as devices, while combination products can carry different requirements. If your team references “Cingal FDA approval status,” verify it directly with your local regulator and the current product labeling rather than relying on secondary summaries.
MedWholesaleSupplies supplies to verified healthcare professionals and clinic accounts.
Where it fits in knee OA care
Viscosupplementation typically sits between conservative therapy and surgical escalation. Many practices place it after a trial of activity modification, PT, weight management, and oral or topical analgesics, while considering patient preference and comorbidities. A combination product may be discussed when a patient has mechanical symptoms plus an inflammatory flare, but the decision is still clinical and individualized. Your role as a clinic leader is to make sure the pathway is consistent: the indication is recorded (for example, “Cingal indication knee OA” in your template), contraindications are screened, and follow-up is structured.
Also plan for the realities of scheduling. A single-visit approach can reduce appointment burden, but it can increase pressure on same-day verification (label checks, consent, and inventory reconciliation). Build that into your rooming and procedure checklists.
What the Combination Tries to Solve: HA + Steroid Concepts
Many clinicians think about Cingal hyaluronic acid triamcinolone as a “two-phase” concept: steroid for shorter-term symptom control and hyaluronic acid for longer-term lubrication and viscosity effects. The hyaluronic acid injection knee benefits most often discussed include improved viscoelastic properties of synovial fluid and potential symptom relief in selected patients. The steroid component is familiar to most teams, but it brings additional considerations such as glycemic impact and infection risk screening.
Because it combines two modalities, staff education should cover both mechanisms at a high level. That helps align expectations and improves documentation quality. It also reduces confusion during adverse-event triage, when timing matters.
Why it matters: Combination pathways can fail when teams document it like HA-only care.
What clinical studies typically report
When teams review Cingal clinical studies, focus on endpoints that map to your practice goals: patient-reported pain and function, time to additional interventions, and safety outcomes. Study designs vary widely. Some compare combination injections to HA alone, steroid alone, saline, or other comparators. Population details matter too, including OA severity, prior injection history, and concomitant therapy. That variability is one reason Cingal effectiveness can look different across summaries. A practical approach is to treat the evidence as supportive but not definitive, then align use with shared decision-making and documented expectations.
Also be cautious with “Cingal duration of relief” claims. Duration can vary by patient factors, disease stage, activity level, and concurrent management. For clinic protocols, it is safer to document that response is variable and to define how you will reassess symptoms and function after the injection.
To place HA options in context, some clinics review overviews like Comparing Hyalgan And Other Hyaluronic Acid Injections and then map those themes to their own formulary.
Safety, Contraindications, and Counseling Points
Safety planning should include both viscosupplementation knee risks and steroid-related risks. For many clinics, the highest-yield step is a consistent pre-procedure screen: active infection, skin breakdown at the injection site, anticoagulation considerations, recent surgery, and relevant allergies. Your checklist should also reflect steroid-specific issues such as diabetes management planning and recent steroid exposures, as appropriate for your practice.
When documenting Cingal contraindications and Cingal warnings and precautions, avoid copying generic text without confirming it matches the product’s instructions for use. Combination products can have specific language on infection, hypersensitivity, and use in certain populations. If your protocol supports it, include a standardized “red flag” script for post-procedure calls to triage possible septic arthritis versus expected post-injection pain flare.
Products are sourced as authentic brand-name items through screened distribution channels.
Adverse reactions your staff should recognize
Cingal injection side effects may include localized injection-site pain, swelling, warmth, stiffness, or transient effusion. Steroid-related effects can include temporary hyperglycemia in susceptible patients. Serious but uncommon complications after any intra-articular injection include infection, hemarthrosis (bleeding into the joint), and severe inflammatory reactions. Train staff to use neutral language: “possible Cingal adverse reactions” rather than “expected,” and to document timing, severity, and associated symptoms. That improves continuity if patients contact an after-hours line or present elsewhere.
Avoid overpromising. Instead of guaranteeing outcomes, document the uncertainty and the plan for reassessment. That framing is especially important for patients who expect a “fast fix” or who have advanced radiographic disease.
Pitfalls to avoid
- Skipping site checks
- Missing glucose counseling
- Incomplete lot capture
- Underdocumenting red flags
- Assuming class-equivalence
Procedure Considerations: Technique, Aftercare, Documentation
Standardizing Cingal administration technique is mainly about consistency, not complexity. Most clinics focus on aseptic technique, correct anatomic approach, and clear role assignment in the room. If your practice uses ultrasound guidance for certain body habitus or difficult anatomy, build that into scheduling and equipment readiness. Also consider “time-out” elements that fit injections: patient identity, laterality, product verification, and allergy review.
Because the combination includes a steroid, it can be helpful to add a brief counseling line about short-term monitoring needs (for example, glucose awareness in people with diabetes), aligned with your policies. This is also where you set expectations about Cingal recovery time: many patients can resume routine activities quickly, but transient soreness can occur. Keep language general and consistent with your handouts.
Documentation that protects the clinic
Build a template that captures: diagnosis and laterality, rationale for injection, prior conservative measures, consent, product identifiers (name, lot, expiration), injection site and approach, and immediate tolerance. Include a follow-up plan and who to contact for urgent symptoms. If your team tracks repeat injection frequency, document the decision logic and reference the label rather than creating a standing interval that could conflict with instructions. For clinics managing multiple viscosupplements, this template also supports clean chart review when patients later ask to compare “last time” versus a new product.
When discussing cingal 4ml with patients, keep the message operational: it is a clinic-administered intra-articular option, and response varies.
Clinic checklist (non-prescriptive)
- Verify product label
- Confirm laterality
- Screen infection risk
- Review allergies
- Document lot/expiry
- Provide aftercare sheet
- Set reassessment timing
Clinic Operations: Verification, Storage, Handling, Inventory
Operational success often hinges on the “quiet” steps: receiving, storage, and traceability. For Cingal storage and handling, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for use and keep those instructions accessible to staff who receive shipments and stock procedure rooms. Do not assume that all hyaluronic acid products share the same storage conditions. If your workflow involves moving stock between sites, define responsibility for chain-of-custody and temperature checks, if required by the label.
Also clarify who can request the product and who can approve it. Many clinics build a simple pre-procedure verification step in the EHR: correct item, correct patient, and correct documentation attached. This reduces last-minute substitutions that can create chart inconsistencies.
Quick tip: Store the IFU link or PDF with your inventory record.
Clinic workflow snapshot
- Verify account credentials
- Confirm product presentation
- Receive and inspect packaging
- Store per labeled conditions
- Stage for procedure day
- Administer per protocol
- Record identifiers in chart
- Report adverse events
For clinics that manage multiple regenerative and injection options, some teams also review Platelet Rich Plasma PRP workflows to keep documentation consistent. If your formulary includes related supplies, keep product references separated from clinical decision-making. Examples of items your inventory team may track include Plasmolifting PRP Gel alongside hyaluronic acid products.
Your supplier may request licensure documentation before processing clinic supply requests.
If you rely on US distribution for multi-site clinics, align receiving procedures across locations.
Comparing Single-Injection Viscosupplement Options
Comparison work is easiest when you separate clinical attributes from operational ones. Clinical teams may weigh evidence quality, patient selection fit, and safety profiles. Operations teams often focus on presentation, storage requirements, documentation needs, and how often the product is used (which affects waste and expiry management). This is where “single injection viscosupplementation” becomes an operational concept as much as a clinical one.
Many clinics evaluate Cingal vs Monovisc, Cingal vs Synvisc-One, or Cingal vs Euflexxa by looking at (1) whether a steroid is included, (2) regulatory labeling, (3) patient preference and prior response, and (4) your ability to follow standardized documentation. For deeper clinical comparisons, articles like Orthovisc Vs Synvisc and Euflexxa Vs Orthovisc can help teams structure discussion points without turning them into promises.
How to compare (practical decision factors)
- Label and status
- Includes steroid or not
- Presentation and volume
- Storage requirements
- Traceability workflow
- Follow-up planning
If your procurement team needs an internal reference list, you can point staff to specific items you stock, such as Monovisc Prefilled Syringe, Orthovisc, or Hyalgan, and then link those items to the correct consent and charting templates.
When your team documents cingal 4ml comparisons, keep the language limited to selection factors and known risks, not predicted outcomes.
Authoritative Sources
For policy and pathway decisions, prioritize primary sources: regulator databases, official labeling, and major society guidelines. These references help you answer compliance questions (what is authorized where), standardize counseling language, and keep staff education current. They also help reconcile differing statements found in marketing materials or secondary blogs.
For neutral, high-level context, start with the following:
- FDA Drugs@FDA database for product status checks
- AAOS guidance on osteoarthritis of the knee
- American College of Rheumatology osteoarthritis guidance
In summary, cingal 4ml is best evaluated as a combination injection pathway with added documentation and safety steps. Build your internal checklist, verify labeling and regulatory status, and compare alternatives using consistent decision factors.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.