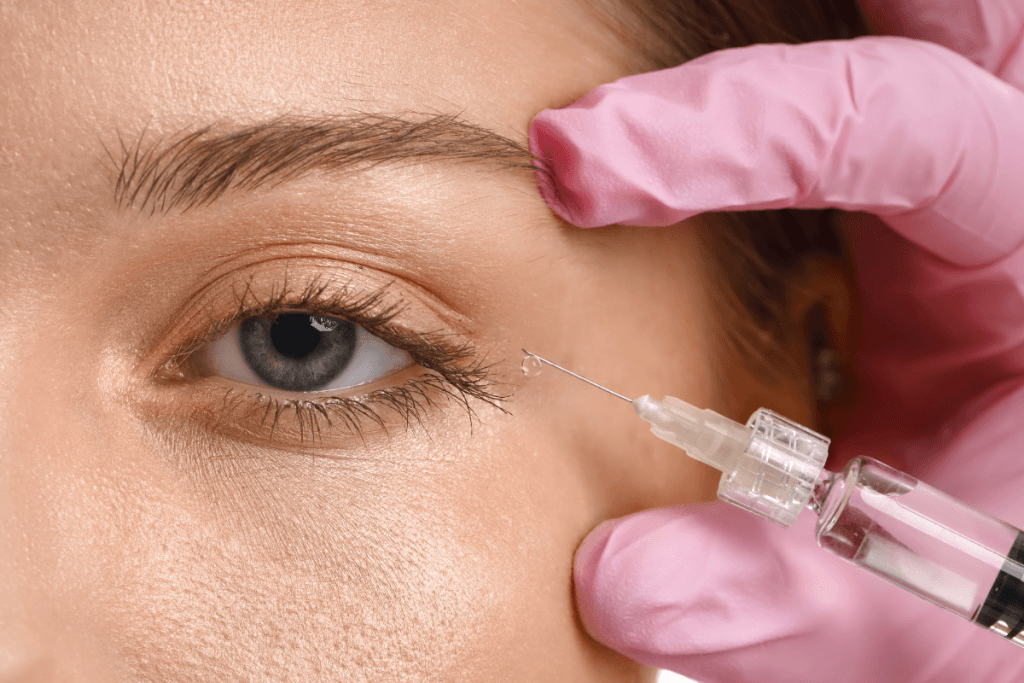
Retina teams are balancing clinical outcomes with operational friction. Anti-VEGF therapy remains a core pathway for neovascular (wet) age-related macular degeneration and diabetic eye disease. Newer formulations can change scheduling, documentation, and inventory needs in subtle ways. This is where eylea hd often enters practice discussions.
This briefing is written for licensed healthcare professionals. It focuses on label literacy, risk conversations, and clinic workflow. It avoids prescribing decisions and patient-specific recommendations. Use it to align your clinicians, billers, and procurement team on shared expectations.
Key Takeaways
- Confirm labeled indications before standardizing clinic pathways.
- Separate procedure coding from drug coding and units.
- Plan for lot/serial documentation and cold-chain-adjacent processes.
- Set patient-facing expectations for common post-injection symptoms.
- Use neutral criteria when comparing anti-VEGF options and switches.
Where eylea hd Fits in Retinal Care
At a high level, this product is an intravitreal anti-VEGF biologic. Anti-VEGF (anti–vascular endothelial growth factor) medicines reduce pathologic retinal and choroidal neovascularization. They also help manage macular edema (retinal swelling) in selected conditions. In clinic operations, the practical questions often center on visit cadence, chair time, and documentation completeness.
The “HD” naming signals a higher-dose formulation of aflibercept, compared with earlier aflibercept presentations used in retina care. Many teams shorthand this as “8 mg vs 2 mg,” but operational planning should still start with the official label. Formulation, presentation, and payer rules can drive different ordering, charge entry, and wastage documentation steps.
It also helps to address a recurring misconception early. Aflibercept is not a corticosteroid (steroid). It is a targeted anti-VEGF therapy, and its risk profile differs from steroid implants or periocular steroids. That distinction matters for staff training and for patient explanations.
MedWholesaleSupplies supports purchasing for verified licensed clinics and healthcare professionals.
Indications and Label Literacy for Retina Teams
Clinicians usually lead with “what is it used for,” while staff focus on what the label requires. Indications can include common retina pathways such as neovascular (wet) age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinal disease (for example, diabetic macular edema and diabetic retinopathy). However, you should confirm the exact approved uses, limitations, and contraindications in the current labeling before building protocols around eylea hd.
Why this matters: your front desk and authorization staff may use the indication language verbatim. Small differences in diagnosis specificity can affect prior authorization, claims edits, and payer requests for chart notes. Align your problem list, imaging documentation, and diagnosis coding to the label language your clinicians intend to support.
Reading the package insert and FDA label
Retina practices often use “prescribing information,” “package insert,” and “label” interchangeably. Operationally, they point to the same source of truth: the manufacturer’s FDA-reviewed labeling. It defines approved indications, warnings, administration route, storage requirements, and presentation details. It also clarifies what was studied and what was not, which helps you avoid accidental off-label messaging in templates and patient handouts.
When building a clinic playbook, treat the label as a requirements document. Pull out the parts that affect workflow: preparation steps, required monitoring language, contraindications that trigger deferral, and adverse event warnings that should appear in your consent. Then map those requirements to who does what in your EHR. For background disease context that supports patient education, you can also share a general overview like Age-Related Macular Degeneration with non-promotional wording.
Quick tip: Store a PDF of the current label in your shared SOP folder.
Injection Visit Expectations and Team Roles
An intravitreal injection visit is a short encounter, but it has many failure points. Most issues are not clinical complexity. They are operational misses: incomplete consent, missing lot numbers, delayed imaging upload, or unclear follow-up intervals in the chart. Consistency reduces rework.
From a patient experience standpoint, staff should normalize what many people feel right after an injection. Transient irritation, foreign-body sensation, tearing, and mild redness can occur after ocular surface prep. Visual phenomena can also be reported, depending on antiseptic use, ocular surface dryness, or intraocular microbubbles. Standardized “what to expect” language reduces after-hours calls and improves documentation quality.
When your clinic introduces eylea hd into the schedule, include your technicians in the rollout. They often field side-effect questions first. Give them a script that stays inside scope: confirm the complaint, document onset, and route urgent symptoms to the clinician per protocol. Policies vary by practice and payer, so keep escalation steps local and documented.
Safety: Adverse Events, Systemic Concerns, and Common Questions
All intravitreal anti-VEGF products carry important ocular safety considerations. Practices should be prepared to counsel on rare but serious risks like endophthalmitis (intraocular infection), retinal detachment, and increased intraocular pressure. You should also plan for how your clinic documents and codes complication assessments when symptoms arise.
Many search queries focus on systemic issues, including “heart problems.” Anti-VEGF agents can have systemic exposure after ocular administration, even when levels are low. Labels often include warnings related to arterial thromboembolic events (such as stroke or myocardial infarction) and hypersensitivity reactions. Your role is not to overstate risk, but to communicate label-based warnings clearly and consistently.
Ocular vs systemic events: how to structure counseling
Separate conversations into two buckets to improve clarity. First, cover eye-local effects: discomfort, redness, transient visual disturbance, and the rare complications that require urgent evaluation. Second, address whole-body warnings at a high level, especially for patients with significant cardiovascular history. This structure helps staff avoid mixing common, self-limited effects with rare, high-acuity events.
Two recurring questions deserve careful framing. “Does it cause hair loss?” is not a typical class expectation for intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy, but patients may attribute unrelated changes to treatment. Document the report, review the label for listed adverse reactions, and encourage clinician follow-up if the symptom persists. “Long-term side effects” is also broad; focus on known risks in the labeling and on the patient’s overall ocular trajectory documented by imaging and visual acuity measures.
MedWholesaleSupplies uses vetted distribution partners to source authentic brand-name medical products.
Comparing Anti-VEGF Options and Switching Considerations
Comparisons like “vabysmo vs eylea vs lucentis” are common, but your clinic’s decision factors are often practical. Start with what is label-supported, what your payers recognize, and what your physicians prefer for specific disease patterns. Then consider visit burden, inventory handling, and claim stability. The most useful comparison is one that your billers and techs can operationalize.
The phrase “difference between Eylea and Eylea HD” is often used to mean dose strength and potential interval flexibility. Avoid making assumptions based on informal summaries. Use the official prescribing information for each product, and keep your internal education neutral. If you are discussing eylea hd alongside alternatives, you can frame it as “aflibercept higher-dose formulation” rather than implying superiority.
| Decision factor | What to verify | Why it affects workflow |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory label | Indications, warnings, presentation, storage | Drives templates, consent language, and staff scripts |
| Dosing language | Label-described regimens and allowable intervals | Impacts scheduling, prior auth cadence, and visit volume |
| Drug identification | NDC/HCPCS mapping and unit reporting | Prevents claim denials and charge-entry errors |
| Switching | Clinical rationale documentation and payer rules | Reduces re-authorization delays and chart requests |
If your team is evaluating a switch pathway, keep the documentation goal simple. Record the reason in plain language, summarize recent imaging findings, and capture prior treatment history. Switching from Eylea to Vabysmo (or vice versa) can also change how your staff handles product selection in the medication list. If you maintain product references for procurement context, keep them clearly separated from clinical decision notes, such as Vabysmo Injection and Eylea English Alternative.
For clinics that rely on US distribution and predictable inventory cycles, consistency in SKU naming and charge mapping reduces downstream corrections.
Documentation, Coding, and Procurement Workflow
Most operational risk sits at the intersection of documentation and billing. Staff may ask for the “eylea hd cpt code,” but the claim typically includes both a procedure code for the intravitreal injection and a separate drug code line. Many practices use CPT 67028 for the injection procedure, then add the appropriate HCPCS code and units for the medication. Exact coding and modifiers depend on payer policy and your local MAC guidance, so verify current requirements before go-live.
Drug line accuracy usually hinges on three items: correct product selection, correct units, and correct linkage to diagnosis. Build a validation step into charge review. This is especially important when you stock more than one anti-VEGF product or multiple presentations of the same molecule, such as Eylea 4 mg Vial for other aflibercept workflows.
Clinic documentation checklist (operational, not clinical)
- Product identification: record NDC and presentation
- Traceability: capture lot number and expiration date
- Administration record: eye laterality and procedure note
- Consent: date, risks discussed, and staff witness
- Imaging: attach OCT/photography references when used
- Billing: procedure code, drug code, units, modifiers
- Inventory: decrement stock and reconcile variances
Procurement teams should also separate “retina injectables” from unrelated periocular aesthetics in cataloging and receiving. This reduces pick-and-pack errors and keeps documentation clean during audits. If your organization also manages inventory in adjacent categories, keep those catalogs distinct, such as Dermal Fillers or Dermal Fillers Product Category, and avoid cross-training staff on look-alike names.
Finally, plan how you will answer “how long does it stay in the system” without guessing. For intravitreal biologics, systemic exposure is generally low compared with systemic administration, but persistence varies by molecule and patient factors. Direct staff to label language and keep a consistent, non-committal script for non-clinician roles. When you operationalize eylea hd, that script should be part of onboarding.
MedWholesaleSupplies supplies brand-name products intended for professional use by licensed healthcare customers.
Further reading can help you standardize patient-facing language across service lines. For example, if your clinic fields questions about periocular skin injectables, keep those education resources clearly separate, such as Croma Philart Eye, Restylane Eyelight, and Philart Eye Overview.
Authoritative Sources
- FDA Drugs@FDA database (search product labels)
- National Eye Institute: Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- National Eye Institute: Diabetic Retinopathy
Well-run retina programs treat labeling, coding, and traceability as clinical safety tools. Use your next product review meeting to align on documentation standards, payer checks, and post-injection communication scripts.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.