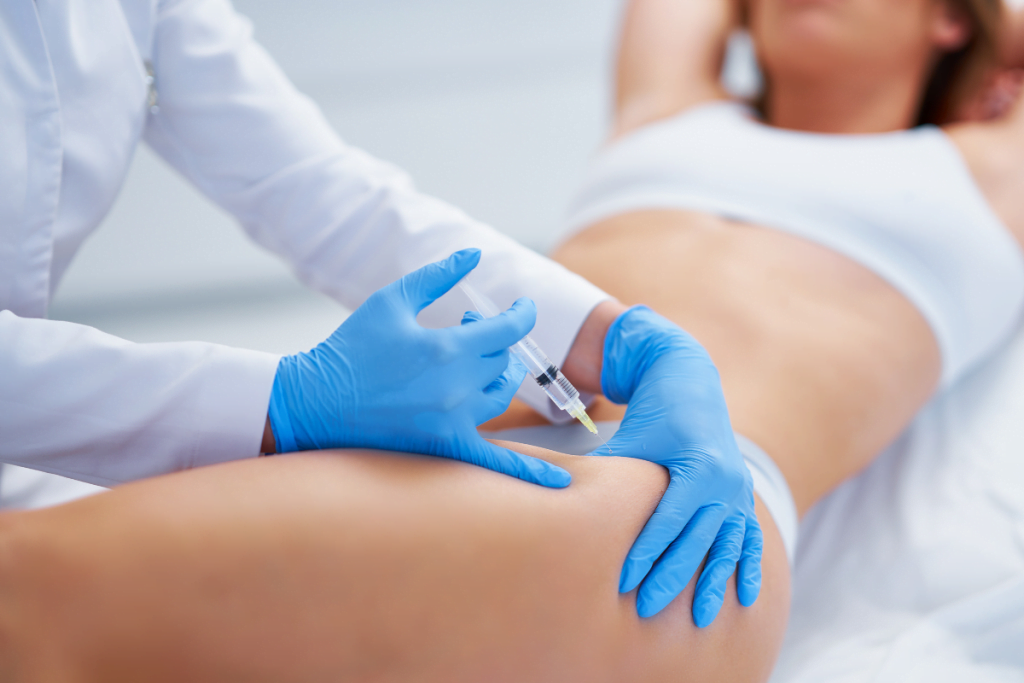
Interest in hyacorp body contouring has grown as clinics expand minimally invasive shape options. For many teams, the key need is clarity. You want a practical view of where hyaluronic acid (HA) body fillers fit, what can go wrong, and what to document.
This guide frames body volumization as a clinic process. It focuses on risk controls, informed consent components, and operational checks. It does not cover dosing, technique specifics, or patient-level medical advice.
Key Takeaways
- Differentiate HA volumizers from collagen-stimulators before counseling.
- Plan for higher consequence complications in larger body regions.
- Build documentation around anatomy, product traceability, and follow-up.
- Set expectations on maintenance and variability in persistence.
Hyacorp Body Contouring in Practice: What It Is
Body contouring with injectable HA typically aims to add volume and adjust contour. Teams often discuss gluteal augmentation (buttock enhancement), hip dips, or other regional shaping. In this context, a “body” gel usually means higher lift capacity and different flow behavior than many facial gels. That difference affects planning, placement depth considerations, and risk assessment.
Clinics also need language that matches what patients search for. You will hear “non surgical butt lift hyaluronic acid” and “hyaluronic acid for buttocks.” Those phrases can obscure the core point: this is still an implantable medical device, delivered by injection, in a high-volume area. Treat it as a higher-stakes procedure from a safety and governance standpoint.
Within the Hyacorp line, you may encounter products positioned for body use, such as hyacorp mlf2 and hyacorp mlf1. You may also see facial-oriented items mentioned online, such as hyacorp fine and hyacorp lips. Keep your counseling clean. Confirm the intended use, anatomical areas, and warnings in the product’s instructions for use (IFU) and local regulations.
Why it matters: Body volumization errors can be harder to reverse and monitor.
Trust cue: MedWholesaleSupplies supports purchasing for licensed clinics and healthcare professionals.
Anatomy, Volumization Goals, and Product Choice
Buttock and hip contour work is not “facial filler, scaled up.” The vascular and fascial anatomy differs, and so does the consequence profile. Your team should map out where you will and will not inject, how you assess symmetry, and how you plan staged sessions when appropriate. These are workflow questions as much as clinical ones.
When you evaluate hyacorp body contouring candidates, also evaluate the clinic environment. Do you have a protocol for emergencies, escalation, and documentation that stands up to audit? Do you have standardized photo capture and follow-up cadence? Consistency reduces variation between injectors and improves continuity if the patient returns with concerns.
Gluteal region considerations
Gluteal augmentation introduces practical constraints. Positioning, privacy, and chaperone practices need to be defined. Your consent should address region-specific risks, including infection risk in an area exposed to friction and pressure. Your post-visit instructions should also reflect that patients sit, sleep, and exercise using the treated area. Many “unexpected” calls after treatment trace back to missed counseling about pressure, swelling, and activity modification.
Formulation differences: MLF2 vs MLF1
Teams often ask about hyacorp mlf2 vs mlf1 because they are marketed as different gels. Rather than relying on a hyacorp filler review or social media summaries, anchor decisions to the IFU, rheology summaries from the manufacturer, and your injector’s experience with similar product classes. Document why a given gel was selected for a given region. If you stock more than one body gel (for example, hyacorp body contouring mlf2 alongside another option), define how selection is standardized across clinicians to avoid inconsistent outcomes and inconsistent counseling.
For broader context on HA behavior across aesthetic indications, see Hyaluronic Acid Impact On Aesthetic Medicine.
HA Volumizers vs Biostimulators: How to Compare
Patients and clinicians often frame “hyaluronic acid buttock injections vs sculptra” as a head-to-head contest. In practice, you are comparing different mechanisms and different follow-up patterns. HA gels provide immediate space-filling volume. Biostimulators (collagen-stimulating injectables) aim to trigger gradual tissue changes over time. Those differences matter for counseling, photography timing, and how you respond to dissatisfaction.
In hyacorp body contouring planning, define the decision factors your clinic uses. Use the same factors in consult notes and consent discussions. That makes your rationale clear and reduces “treatment drift” across providers.
How to compare (clinic decision factors)
- Mechanism of change: immediate fill vs gradual collagen response.
- Reversibility planning: consider options if results disappoint.
- Follow-up needs: swelling checks, asymmetry review, touch-up planning.
- Risk profile: include vascular compromise and inflammatory reactions.
For a broader overview of other contouring modalities some clinics offer, review Body Contouring Treatments and, when appropriate, compare to non-filler options like Mint PDO Threads.
Risk Management: Contraindications and Complications
Risk language should be explicit and operational. Clinics should track expected reactions, like swelling and tenderness, and define thresholds for escalation. For search-aligned language, many teams field questions about hyaluronic acid buttock injections side effects. Your internal SOP should translate that question into: “Which symptoms are expected, which are urgent, and how do we document response?”
For hyacorp body contouring, many risk controls look like familiar dermal filler controls, but the consequences can be larger. Concerns include infection, nodules, migration, inflammatory reactions, and tissue compromise from inadvertent intravascular injection. If you use hyaluronidase in your practice for HA complications, ensure staff training, storage per labeling, and an on-call escalation pathway are in place.
Contraindications and patient screening
Do not assume hyacorp contraindications are identical to those for every HA filler. Confirm the IFU. In general terms, clinics often screen for active infection near the treatment area, certain hypersensitivities, uncontrolled systemic illness, and situations where immune response is altered. Screening should also include prior permanent fillers or unknown injected materials, especially in the gluteal region. Document the history clearly, even when the patient is unsure.
Common pitfalls (process-focused)
- Vague consent: no clear complication escalation plan.
- Poor photos: inconsistent lighting, stance, or landmarks.
- Weak traceability: missing lot, expiry, or injector documentation.
- Overreliance on anecdotes: substituting “reviews” for IFU guidance.
When you discuss hyacorp safety and hyacorp risks with patients, keep claims conservative. Use probability language carefully. Avoid promising specific persistence, symmetry, or “before and after” magnitude.
Trust cue: Products are obtained through vetted distribution partners to support brand authenticity.
Aftercare, Monitoring, and Photo Documentation
Aftercare should be standardized, written, and easy to follow. Many clinics search for “hyaluronic acid buttock injections aftercare” templates. Use that interest to improve internal consistency. Provide guidance on expected swelling, bruising, and pressure sensitivity, plus what changes trigger urgent contact. Align instructions with your infection control policies and documentation practices.
With hyacorp body contouring, follow-up is also a data problem. Patients will judge outcomes in motion, different clothing, and different lighting. Your clinic can reduce friction by setting photo standards. Use fixed landmarks, consistent posture, and the same camera settings. Document “hyacorp body contouring before and after” images as clinical records, not marketing assets, unless separate consents apply.
Documenting change responsibly
“Before and after” discussions often become binary: either the patient sees change or does not. In reality, swelling, activity, and weight fluctuation can shift appearance. Make your chart reflect those variables. Include baseline measurements when your clinic uses them, and note confounders like menstrual cycle-related water retention or recent exercise changes. If patients ask for “hyacorp filler for buttocks before and after” examples, consider showing only de-identified cases that match body type and treatment plan, with clear disclosures about variability.
For teams also handling facial injectables, keep documentation conventions consistent across services. You can cross-train staff using examples from Juvederm Voluma Lift And Contour as a contrast in anatomy and photo angles.
Quick tip: Use the same room, marks on the floor, and camera height.
Procurement and Clinic Workflow Snapshot
Body fillers add operational load. Your receiving process should confirm packaging integrity, lot and expiry capture, and storage requirements per labeling. Procurement teams should also set rules for who can request and release stock, especially when multiple injectors work across sites. If you use reliable US logistics for clinic resupply, align delivery scheduling with receiving staff coverage to avoid gaps in documentation.
In hyacorp body contouring programs, traceability is not optional. If a patient reports swelling weeks later, you need to retrieve the exact product details quickly. That includes lot, expiry, quantity used, anatomical sites, and injector. Link this to your adverse event reporting pathway and your medical director review process.
Clinic workflow snapshot (high-level)
- Verify licensure and authorized buyers.
- Document product selection rationale and consent elements.
- Receive stock and record lot/expiry.
- Store per IFU and rotate inventory.
- Administer per clinic SOP and chart standardized details.
- Schedule follow-up and record outcomes and concerns.
Procurement checklist (documentation-forward)
- Lot and expiry: captured in EHR and inventory.
- Chain-of-custody: who received and who released.
- Condition on arrival: packaging intact, anomalies noted.
- Returns policy: documented and staff-trained.
- Recall readiness: ability to identify affected patients.
For clinics stocking product examples, see Hyacorp Body Contouring MLF 2 and Hyacorp Body Contouring MLF 1. For broader service-line planning that may include non-filler modalities, some practices also review resources on Aqualyx Treatment and Fat Dissolving Injections. If your clinic also dispenses weight management items, browse the Weight Loss hub to keep categories organized.
Further reading: For a focused discussion on buttock use-cases and safety framing, see Hyacorp Filler For Buttocks.
Authoritative Sources
- FDA: Dermal Fillers (overview and safety topics)
- American Academy of Dermatology: Dermal fillers overview
Recap: Treat body HA volumization as a program, not a single procedure. Standardize counseling, photography, and traceability. Use IFUs and reputable safety resources when you compare options or respond to complications.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.