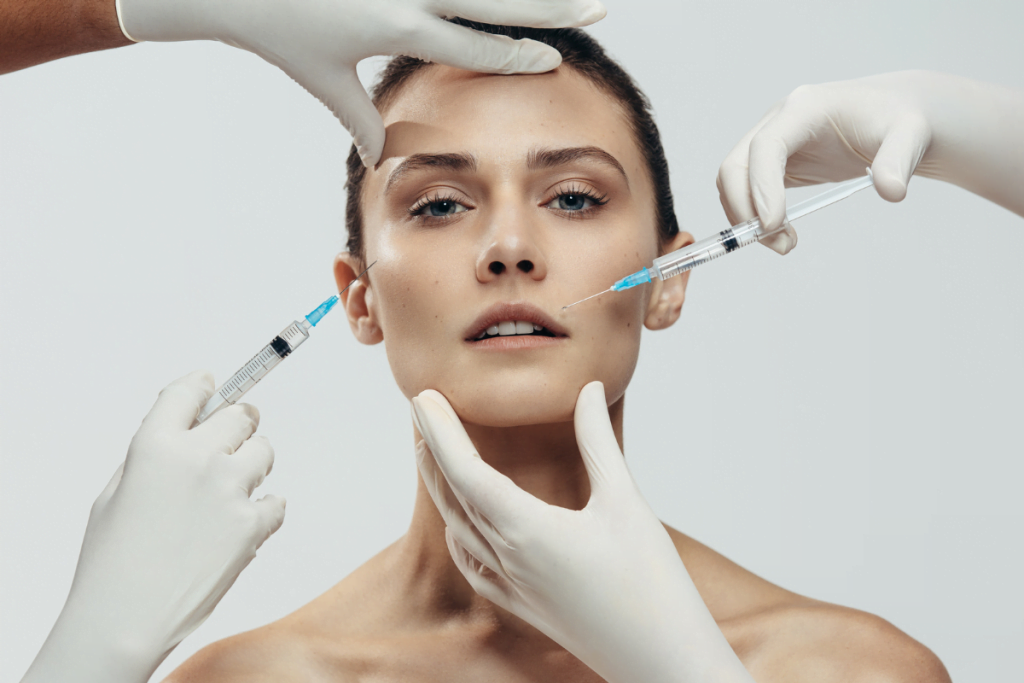
Clinic teams field constant questions about neuromodulators for facial lines. Many requests start as “Botox,” but the category is broader. This guide frames botox options in a clinic-facing way, with emphasis on labeling, comparability, and operational fit. It is written for licensed healthcare professionals, not direct-to-consumer decision-making.
MedWholesaleSupplies works with licensed clinics and credentialed healthcare professionals.
Quick tip: Treat each botulinum toxin label as its own product standard.
Key Takeaways
- Start with the label: indications, warnings, and storage differ.
- Units are product-specific; do not convert across brands.
- Brand names vary by region; confirm the exact presentation.
- Operational controls matter: lot tracking, documentation, and sourcing checks.
What Changes When You Compare Neuromodulators?
In aesthetic medicine, “Botox” is often used as shorthand for botulinum toxin injections. Clinically, you are selecting a specific biologic product with its own labeling, manufacturing controls, and instructions for preparation and storage. That distinction matters for training, documentation, and patient communication.
When clinics evaluate botox options, it helps to separate three ideas: the active ingredient class (botulinum toxin), the product presentation (vial, potency units, excipients), and the approved use cases on the local label. Two products can both be “toxin type A” and still be non-interchangeable in dosing units, handling steps, or labeled indications. These differences affect protocols and error-prevention steps in busy treatment rooms.
Type A neuromodulators, explained in plain language
Most cosmetic neuromodulators used for facial wrinkles are botulinum toxin type A. At a high level, they reduce muscle activity by blocking acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction (the nerve-to-muscle signaling site). Patients may describe this as “relaxing” a muscle or “softening” a line. Clinicians and staff should keep the language precise: these products are prescription biologics, not interchangeable commodities. Product names can also differ outside the U.S., so the same manufacturer may use different branding in different markets.
To support staff education, consider a one-page internal reference that lists each product’s full nonproprietary name, the exact vial size used in your clinic, storage requirements, and a reminder that potency units are product-specific. For broader context, see the internal overview on Top Botulinum Toxin Brands.
Botox Options: Brands, “Toxin Type,” and Labeling
Brand selection starts with accurate naming. “BOTOX” and “BOTOX Cosmetic” are distinct labeled products, and clinics should document the exact item administered. Comparable neuromodulators include Dysport and Xeomin, among others, but they are not the same product even when used for similar aesthetic goals. A practical first step is to align your consent forms, EMR picklists, and inventory records to match the name on the carton and vial.
For teams standardizing an inventory list, it can help to keep product education linked to a single internal resource per brand. Examples on MedWholesaleSupplies include product references for Botox, Dysport, and Xeomin. For a deeper operational overview, the article Botox Gold Standard Overview can support staff onboarding and terminology alignment.
International branding can add friction. Some products are marketed under different names in different regions, and local approval status may differ. If your clinic operates across jurisdictions, or treats traveling patients, build a habit of confirming the specific product name, manufacturer, and labeling language rather than relying on umbrella terms like “top 10 botox brands.” For operational safety, the goal is not a popularity list. The goal is traceable, correctly documented stock that matches your training and protocols.
Dysport vs Botox vs Xeomin: Interpreting Differences for Clinics
Comparisons like “Dysport vs Botox vs Xeomin” are common in consult conversations and staff training. From an operations standpoint, the most important principle is straightforward: potency units are not interchangeable between products. Your protocols should reflect that by separating ordering, storage, reconstitution instructions, and EMR documentation for each brand.
MedWholesaleSupplies sources brand-name medical products through vetted distributor channels.
| Clinic-facing factor | What to verify on the label | Why it affects workflow |
|---|---|---|
| Product identity | Exact proprietary and nonproprietary name | Prevents selection and documentation errors |
| Units and preparation | Units per vial and preparation instructions | Supports standardized in-room setup and checks |
| Storage conditions | Temperature and handling instructions | Guides receiving, storage, and excursion management |
| Indications and warnings | Labeled indications, contraindications, boxed warnings | Shapes consent language and escalation pathways |
Clinics also encounter “Dysport vs Botox units” questions. Avoid informal conversion charts unless they are part of an approved internal training standard anchored to the official label and medical director oversight. Staff should be trained to respond consistently: the products are different, and the labeling governs how the clinic uses and documents each one.
If you want more detailed brand-to-brand discussion for internal education, use focused reading rather than chairside summaries. Two useful references are Botox vs Dysport Analysis and Xeomin and Botox Comparison.
Injection Planning and Documentation Basics
Many online searches focus on “botox injection sites face diagram” and before-and-after galleries. In clinic operations, the more useful translation is documentation quality. You want consistent mapping of treatment areas, product identity, lot number, and any reconstitution details your policy requires. This supports continuity of care, internal review, and adverse-event follow-up if needed.
When patients ask about the “best places to get botox on face,” they are often describing common cosmetic areas rather than clinic location. Teams can respond in plain language that typical areas include the glabella (between the brows), forehead lines, and lateral canthal lines (“crow’s feet”). Some practices also treat lower-face regions, but those decisions depend on training, product labeling, and careful functional assessment.
Why it matters: Perioral placement can affect speech and oral competence.
Queries like “botox around the mouth before and after” can create unrealistic expectations if staff rely on photos alone. Consider a standard intake approach that captures the patient’s functional priorities, occupation-related needs, and any relevant medical history. Then make sure your records clearly link what was discussed to what was administered. For team education, Dysport In-Depth Look can be a helpful model for how to summarize a neuromodulator’s clinical and operational considerations without turning it into marketing.
Pitfalls that drive preventable errors
- Mixed vials in-room: separate setup trays by product.
- Incomplete lot capture: record lot and expiration every time.
- Ambiguous charting: document the exact brand and indication.
- Overreliance on photos: tie expectations to assessment notes.
- Unit confusion: reinforce non-interchangeable units in training.
Alternatives to Toxin Injections: What Clinics Can (and Can’t) Promise
Patients and even staff may ask, “what is the best alternative to botox.” The right answer depends on the concern being treated: dynamic lines, static wrinkles, skin texture, laxity, or volume loss. In practice, alternatives are often complementary rather than direct replacements. Examples include dermal fillers (for volume), resurfacing and energy-based devices (for texture and tightening), and skincare regimens that support barrier function and photoprotection.
Requests for a “permanent alternative to botox” usually reflect a desire to reduce maintenance visits. For some patients, surgical options (such as brow procedures) may address an underlying anatomic concern more durably, but they are not the same intervention as neuromodulator therapy. Framing matters: toxin injections are typically temporary, and “permanent” should be treated as a counseling and expectations topic rather than a product comparison.
“At home botox alternative” and “natural alternative to botox for wrinkles” searches are common. Your staff can communicate a clear boundary: topical products cannot replicate prescription neuromodulator pharmacology. Some topicals may improve hydration or the appearance of fine lines, but they do not block neuromuscular transmission. Also consider building a policy for handling patients who mention unregulated injectables or internet-sourced products. The safest clinic stance is to discourage unsupervised use and reinforce licensed medical pathways.
For a structured discussion of why neuromodulators are often chosen in aesthetic plans, see Why Botox Is Preferred. For teams comparing expectations around different products, Xeomin Before and After Overview can support internal counseling scripts and consent language.
Procurement and Compliance Checklist for Clinics
With botox options, procurement is not just a purchasing decision. It is a compliance workflow that protects patient safety and reduces operational risk. Your goal is to ensure the product is authentic, traceable, stored correctly, and documented in a way that supports clinical review. Clinics also benefit from separating “education content” from “inventory controls,” so staff know where to find the current policy version.
MedWholesaleSupplies focuses on authentic, brand-name medical products intended for professional clinical use.
Clinic procurement checklist (operational, not clinical)
- Credentialing on file: verify licensure and authorized purchasers.
- Traceability: keep invoices and receiving records.
- Lot control: log lot, expiration, and disposition.
- Storage SOP: follow labeled storage requirements.
- Excursion process: document and quarantine when needed.
- Access control: restrict inventory to trained staff.
- EMR alignment: match product names to picklists.
- AE pathway: define reporting and escalation steps.
For sourcing and selection, a category hub can help teams compare presentations without relying on memory. You can browse the Botox Category to keep internal lists consistent. If your operations include US distribution, confirm receiving hours, storage space, and who signs for biologics.
A simple workflow snapshot can clarify roles across front desk, clinical, and inventory teams: verify account credentials → document purchase and receiving → store per label → prepare per protocol → administer under prescriber oversight → record in the medical record → reconcile inventory and lots. Policies vary by facility and jurisdiction, so keep this as a template and adapt it to your compliance requirements.
Authoritative Sources
Use official labeling and regulator resources to anchor training and policies. These links support product-specific verification and safety language.
- For U.S. labeling and approvals, consult FDA Drugs@FDA product database.
- For boxed warnings and class safety communications, review FDA Drug Safety and Availability.
- For adverse event reporting pathways, see FDA MedWatch reporting program.
Further reading: revisit your internal protocol whenever you add a new neuromodulator brand, change staffing, or update documentation templates. Reliable US logistics may reduce variability, but your storage and documentation controls remain the key safeguards.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.