Aesthetic practices often field the same question: what is belotero, and how does it differ from other hyaluronic acid (HA) gels. For clinic teams, the answer is not only clinical. It is operational. Product selection affects consent language, complication readiness, photo documentation, and inventory controls. It also shapes how you set expectations when patients reference “before and after” images online.
This guide focuses on practical, label-respecting concepts. It avoids technique and dosing specifics. Use it to align your clinical team, procurement staff, and compliance processes around a consistent approach to HA dermal fillers.
Why it matters: Small workflow gaps can become big charting and safety problems.
Key Takeaways
- Define the gel: HA fillers are temporary, reversible volume-and-line correctors.
- Match the variant: Softer vs firmer gels influence placement goals and counseling.
- Plan for risk: Have protocols for vascular events and late-onset reactions.
- Document tightly: Track lot numbers, locations, and patient communications.
- Source responsibly: Verify legitimacy through controlled, clinic-only channels.
What Is Belotero: Clinical Overview and Fit
Belotero is a brand family of HA dermal fillers. Like other HA gels, it is used in aesthetic medicine to address lines, contours, and volume deficits. HA is a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan (a water-binding skin molecule). In filler form, it is processed into a gel designed to integrate into tissue and provide structural support. The practical takeaway is simple: these are medical products with real risk, not cosmetic “touch-ups.”
From an operations viewpoint, HA fillers sit at the intersection of elective care and medical-device discipline. Your policies should treat them like other implantable or injectable supplies. That includes controlled access, chain-of-custody awareness, and clear patient communication. Even when outcomes are subtle, the documentation and safety expectations are not.
Trust cue: Access is limited to verified clinics and licensed healthcare professionals.
Understanding Product Variants: Softer to Firmer Gels
Most practices do not choose “a filler.” They choose a specific gel behavior for a specific task. That is where product variants matter. When staff ask what is belotero in day-to-day terms, you can frame it as “a set of HA gels with different handling and support characteristics.” Clinics often carry more than one variant so they can match tissue needs and aesthetic goals without forcing one product into every indication.
How to read gel properties (without over-promising)
Marketing terms can be misleading if they are treated like universal performance claims. Instead, anchor your selection discussions on broad, defensible concepts: softness, lift capacity, spread, and how the gel may integrate in superficial or deeper planes. Rheology (flow and deformation behavior) can be a helpful lens, but it does not replace training and experience. Patient factors also matter, including skin thickness, prior procedures, and edema tendency. Keep comparisons descriptive, then defer to the official instructions for use (IFU) and your medical director’s protocols.
Examples clinics may stock
Within this product family, you may see references to belotero balance, belotero intense, belotero volume, and belotero revive, along with lip-focused presentations. In practical terms, teams use these names to communicate relative gel firmness and intended use cases. Some presentations include lidocaine, which can affect counseling and allergy history documentation. Your preference card should list the specific SKU, its intended clinic use, and any contraindication reminders pulled from the IFU.
If you are standardizing your formulary, start by mapping each variant to a narrow set of goals. Overly broad stocking increases expiry risk and increases selection errors. For background on category-level differences, see Types Of Dermal Fillers and the Dermal Fillers Editorial Hub.
Treatment Zones, Patient Language, and Expectation Setting
Patient requests often arrive as internet shorthand. You will hear “belotero lips,” “under-eye filler,” or requests for “belotero before and after” photos. Clinic teams should translate those requests into structured clinical conversations. That means clarifying the aesthetic objective, screening medical history, and documenting what the patient expects to see change. Standardized photography helps, but it must be paired with consistent lighting, positioning, and timing to avoid misleading comparisons.
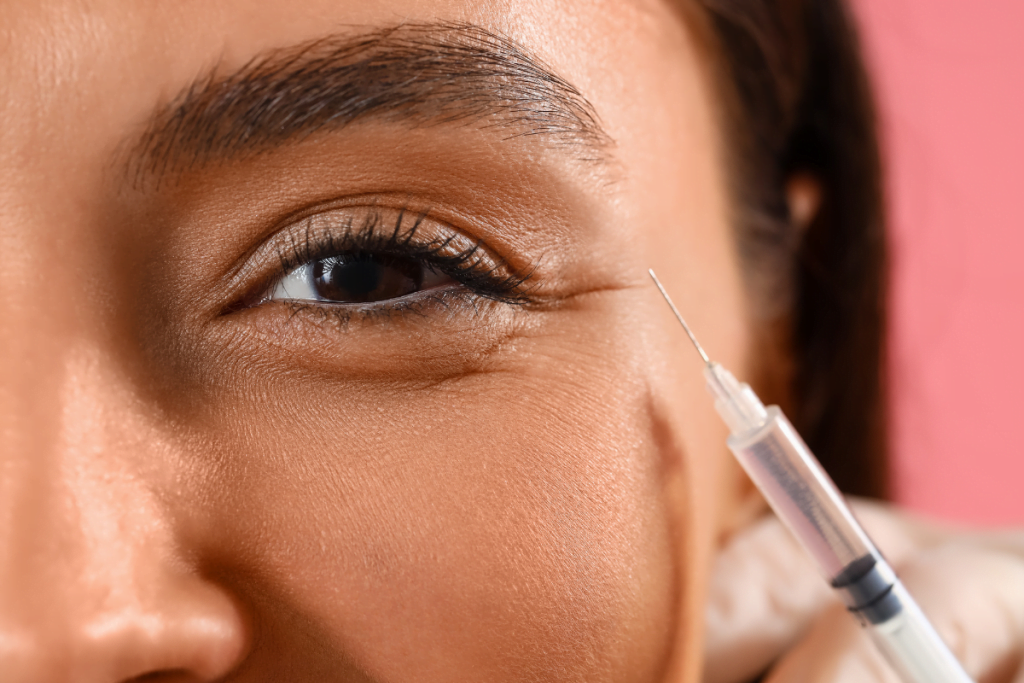
Under-eye discussions require extra care. Patients may use the phrase belotero under eyes to describe dark circles or hollowing, but “dark circles” can reflect pigment, vascular show, or shadowing from anatomy. Your intake should separate the symptom description from the anatomical assessment. It also helps to document what risks you reviewed, since the periorbital region is sensitive and complications can be more consequential.
Using “reviews” and “before/after” content safely
Online belotero filler reviews and photo galleries can influence expectations. That influence is not inherently negative, but it can distort timeframes, degree of change, and normal recovery. Consider adding a short chart template line that notes: (1) what the patient referenced, (2) what you clarified, and (3) what uncertainties remain. If your practice shares images, ensure you have consent specific to photography use, not just procedure consent. For broader counseling language, the article Myths And Misconceptions can support staff training.
Many practices also benefit from a “plain-language script” that explains swelling, bruising, and asymmetry in the early period. Pair that with your standard after-visit summary and escalation instructions. The goal is consistency, not reassurance.
Comparing Hyaluronic Acid Fillers in Your Formulary
Clinical teams frequently ask for “belotero vs juvederm” or “belotero vs restylane” comparisons. A useful clinic response is to shift the discussion from brand-to-brand claims to decision factors you can defend: labeled indications, gel characteristics, reversibility planning, and internal training familiarity. Patients may also bring “lip filler reviews” into the room, so staff should be ready to explain why a different HA gel may be selected for the same general area.
Why it matters: Formulary decisions affect emergency preparedness and standard operating procedures.
| Decision factor | What to standardize | What can vary |
|---|---|---|
| Labeled use and IFU | Approved indications, contraindications, warnings | How you present patient-friendly explanations |
| Gel behavior | Internal definitions for “soft,” “medium,” “firm” | Which variant you assign to which aesthetic goal |
| Reversal planning | Hyaluronidase (HA-dissolver) availability and protocol | Escalation pathways by site and staffing model |
| Patient experience | Consent language, photo standards, follow-up touchpoints | Your routine comfort measures and scheduling |
| Supply chain controls | Lot tracking, storage checks, expiry rotation | Par levels by location and provider preference |
If you want a structured way to discuss alternatives, your team may also reference comparative frameworks like Sculptra Vs Juvederm (as a decision-process example), even when the product class differs. For a Belotero-specific discussion that stays general, see Belotero Balance For Fine Lines.
Trust cue: Inventory is sourced through vetted distribution partners, not informal secondary channels.
Safety, Side Effects, and Risk Planning
Set expectations that adverse events exist even with common procedures. Patients will search “belotero side effects,” but your clinic needs a structured framework that covers all HA filler risks. Common reactions can include transient swelling, tenderness, bruising, and lumps. Less common but serious complications can include infection, inflammatory nodules, hypersensitivity reactions, and vascular compromise. Vascular occlusion (blocked blood flow) is a time-sensitive emergency that requires immediate recognition and response per your protocol and training.
When patients ask what is belotero in safety terms, a concise answer is: “an HA gel that is temporary and can be dissolved, but still carries injection-related risks.” That statement supports informed consent without overpromising reversibility or outcomes. Keep your emergency resources aligned with the products you use, and run periodic drills for triage, documentation, and escalation. Late-presenting concerns should be documented carefully, including timing, associated systemic symptoms, and any recent dental work or illness that could be relevant to inflammation.
Aftercare planning matters too. Standard belotero aftercare instructions should be written for comprehension and consistency. Align them with your medical director’s guidance and the product IFU. The article Post-Treatment Care Essentials can help you audit your handouts for clarity.
Clinic Operations: Sourcing, Documentation, and Storage
A strong filler program relies on disciplined back-office steps. Start with sourcing controls that match the clinical risk profile. Maintain a short list of approved suppliers and require documentation that supports authenticity and traceability. Many clinics prefer suppliers that work specifically with licensed medical accounts and brand-name inventory. If you run multi-site operations, align naming conventions across locations so SKUs are not confused at intake or during time-outs.
Use the dermal filler category structure to support purchasing and training. Your procurement team can cross-check standard options via the Dermal Fillers Product Category. When you need to reference a specific presentation in internal documents, link to the exact SKU for staff clarity, such as Belotero Balance With Lidocaine, Belotero Volume With Lidocaine, or Belotero Lips Contour With Lidocaine. Keep clinical decision-making separate from inventory referencing.
Quick tip: Build a one-page SKU sheet with photos, storage notes, and lot-label examples.
Clinic workflow snapshot
- Verify: confirm licensure requirements and account authorization.
- Document: store invoices, lot numbers, and expiry dates.
- Receive: inspect packaging integrity and match quantities.
- Store: follow labeled conditions and restrict access.
- Prep: use a standardized time-out and product verification step.
- Record: chart product, lot, injection sites, and patient education.
- Review: reconcile inventory and investigate discrepancies.
Procurement checklist (operations-focused)
- Supplier vetting: confirm the distributor relationship and documentation pathway.
- Lot traceability: ensure lots link from invoice to patient record.
- Expiry rotation: implement FEFO (first-expire, first-out) processes.
- Storage audit: log conditions per manufacturer labeling.
- Training alignment: keep protocols consistent across providers.
- Recall readiness: maintain a patient-listing workflow by lot number.
Common pitfalls include mixing patient-facing “reviews” with clinical selection, allowing ad-hoc SKUs into inventory, or failing to reconcile opened units. Another frequent issue is incomplete lot documentation when a patient returns with concerns. Audit your charts quarterly for completeness. If you source through US distribution channels, confirm your receiving team understands how to document chain-of-custody and resolve discrepancies.
Trust cue: Brand-name products are supplied for professional use with standard verification steps.
Authoritative Sources
For policy writing and staff training, prioritize primary sources. Use the product IFU for each specific presentation, and update protocols when labeling changes. When discussing complications, rely on regulator and specialty-society guidance rather than anecdotal content.
The links below are helpful starting points for general dermal filler safety. They are not a replacement for your internal clinical governance or manufacturer labeling.
- FDA overview of dermal fillers (soft tissue fillers)
- American Academy of Dermatology information on dermal fillers
- American Society for Dermatologic Surgery overview of soft tissue fillers
Further reading can also be operational. Lip requests are a high-volume driver of schedule pressure, so it helps to train staff on intake language and consent documentation. See Types Of Lip Fillers for a framework that supports consistent communication. If your practice depends on reliable US logistics, build redundancy with clear par levels and reorder triggers.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.