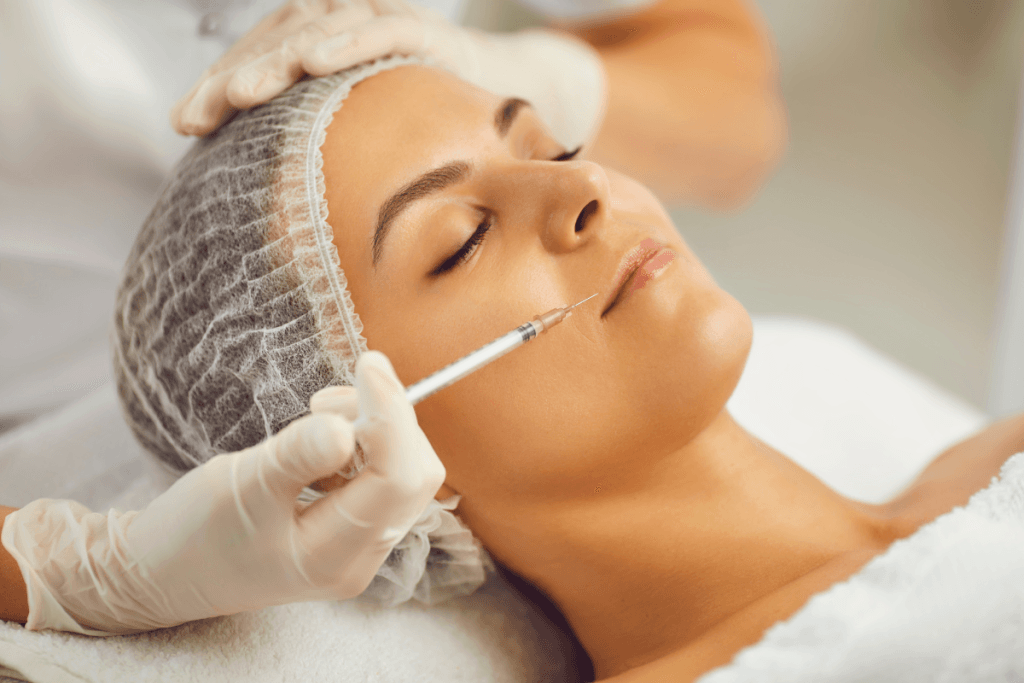
In aesthetic practice, “natural” is not a marketing term. It is a measurable outcome. You are balancing facial proportion, soft-tissue support, and patient expectations. Stylage filler is often discussed in that context because it sits within the hyaluronic acid (HA) filler (gel-based volume and contour) category used for facial shaping.
This guide focuses on what drives durable, natural-looking outcomes in day-to-day clinic work. It does not replace product labeling, training, or your clinical judgment. It highlights formulation concepts, common treatment-area considerations, and risk-aware workflow steps that support consistent results.
Supply access is limited to verified licensed healthcare accounts.
Key Takeaways
- Natural outcomes come from planning, product selection, and technique alignment.
- Crosslinking and additives shape gel behavior and handling feel.
- Longevity depends on anatomy, depth, and patient variability.
- Clinic documentation supports traceability and safer follow-up workflows.
- Comparisons across HA lines work best with label-first criteria.
Stylage filler in Clinic Practice: What Drives Results
Long-lasting, natural results usually depend on a few controllable clinic variables. Start with clear goals and a conservative plan. A “natural” endpoint often means restored support and smoother transitions, not maximal volume. That is easiest to achieve when you define the primary deficit (structure, volume, or hydration) and match it to a gel profile and placement approach.
Outcome consistency also depends on how you standardize evaluation. Use baseline assessment templates, consistent photography, and a structured follow-up note. When patients bring social media references, translate that into objective targets. Document what you did and why, including the area, plane, and device selection. This supports continuity if another clinician sees the patient later.
Why it matters: Standardized documentation reduces confusion when swelling or asymmetry prompts a follow-up call.
Formulation Concepts: HA, Excipients, and Crosslinking
Most HA dermal fillers share a familiar backbone: crosslinked hyaluronic acid suspended in a buffered solution. Even within the same category, gels vary in elasticity (how well the gel resists deformation), cohesivity (how well it holds together), and viscosity (how thick it feels). Those properties influence how a product may behave in different tissue planes and facial zones.
When clinicians search for Stylage filler ingredients, they are usually trying to predict handling and patient experience. Many HA fillers are offered in versions with and without a local anesthetic such as lidocaine. Some also include antioxidants in the formulation. One example is mannitol in Stylage filler (a sugar alcohol often used as an antioxidant excipient). In practice, additives may affect stability and perceived post-treatment reactivity, but your best reference remains the official instructions for use (IFU) for the specific presentation you stock.
What “IPN-Like” Crosslinking Is Trying to Solve
Clinicians may see references to Stylage filler IPN-Like crosslinking. In broad terms, crosslinking is how manufacturers connect HA chains to form a more durable gel. “IPN-like” typically refers to an interpenetrating network concept, where polymer chains are arranged to create a stable, intertwined structure. The practical takeaway is not a single “better” outcome. It is that crosslinking design can change firmness, spread, and integration. That affects product choice by region, not just by brand. When onboarding a new HA line, align your training with how the gel is intended to be placed and layered.
Country-of-origin questions also come up (“Stylage filler made in …”). For procurement teams, the operational answer is simple: verify country-of-manufacture and regulatory status from the packaging, IFU, and supplier documentation for your market. Avoid relying on screenshots or secondary listings.
Area Selection: Matching Gel Behavior to Facial Zones
When teams ask about the best areas for Stylage filler, they are usually asking a broader question: where does a given gel profile integrate smoothly, and where does it risk visibility or irregularity? In general, thicker soft tissue and deeper planes often tolerate a wider range of gel behaviors. More mobile or thin-skinned areas require tighter control, conservative volume, and careful device selection.
Common clinic discussions include Stylage filler for cheeks (midface support and contour) and Stylage filler for nasolabial folds (transition smoothing and structural support). The operational point is to keep the plan anatomically driven. In many faces, midface support changes the fold more safely than chasing the fold directly. Your notes should reflect that logic, including baseline asymmetry and any prior filler.
Lips and Perioral Work: Plan for Motion and Edema
Stylage filler lips discussions tend to center on shape control and predictability. Lips are highly vascular and mobile, and swelling can change the early look. That makes patient counseling and photo timing essential. Define whether the target is border definition, body volume, or oral-commissure support. Then choose an approach that fits your training and the product’s intended use. If you stock multiple options within a line, keep a simple internal guide for when you reach for a softer gel versus a more structural one, and document the rationale each time.
Periorbital Caution: Thin Skin, Tight Tolerances
Interest in Stylage filler for tear troughs reflects a real demand, but it is also a high-scrutiny area. Thin skin increases the risk of visibility, contour irregularities, and prolonged edema. For clinics, the key is not “can it be done,” but “is the workflow ready.” That includes careful candidacy screening, consent language aligned with known risks, and a clear plan for escalation if a patient reports pain, blanching, or vision symptoms after treatment.
Longevity and Follow-Up: Setting Expectations Without Overpromising
How long does Stylage filler last is a common question from both patients and staff. A realistic clinic answer is that longevity varies. It depends on product selection, injection depth, area mobility, and individual metabolism. Lips often behave differently than the midface. High-motion areas may appear to “wear” sooner, even when product remains present. Align follow-up timing with your documentation needs, not a promised duration.
Build a simple internal script for the early healing window. Swelling and bruising can occur with any HA filler treatment, and swelling often peaks within the first few days. Your front-desk and clinical teams should give consistent guidance on what is expected versus what warrants prompt clinical review, based on your protocols and the product’s labeling. If you publish practice education materials, keep them label-aligned and avoid absolute timelines.
Quick tip: Use consistent lighting and camera distance for before-and-after photo comparisons.
Online content influences expectations, including Stylage filler reviews before and after. Treat these as anecdotes, not evidence. Before-and-after images vary widely by angle, edema, and retouching. In clinic, define your photography standards, keep images timestamped, and record any interim events (recent dental work, infections, or new skincare devices) that could confound a comparison. If your team needs a broader refresher on duration counseling, see How Long Lip Fillers Last.
Safety Profile Planning: Contraindications, Side Effects, and Risks
Stylage filler safety conversations should be framed like any HA filler risk review. Start with labeling, then layer your clinic’s clinical governance on top. Contraindications can include known hypersensitivity to ingredients, active infection or inflammation at the treatment site, and situations where elective procedures are deferred by clinical judgment. Many practices also screen carefully for prior filler history, autoimmune or inflammatory conditions, and recent procedures that may change tissue response. Policies vary, so record what you ask and why.
For day-to-day operations, most questions are about Stylage filler side effects. Expected short-term effects can include swelling, tenderness, redness, and bruising. The more important planning step is how your clinic identifies and escalates potential complications. Align your team on who fields calls, what symptoms trigger immediate clinician review, and what documentation is required in the medical record.
Complications to Plan For (Even If Rare)
Every injector should be prepared for time-sensitive adverse events associated with dermal fillers, including vascular compromise. Clinics also encounter nodules, delayed inflammatory reactions, and suspected infection. Preparation is not only clinical; it is operational. Keep protocols accessible, maintain staff training records, and document product identifiers (lot and expiry) at the point of care. If you use both needle and cannula approaches, document cannula vs needle for Stylage filler decisions as part of technique rationale, since device choice can affect bruising patterns and risk profile. When in doubt, defer to training guidance and local regulations.
- Incomplete history: missed prior filler or procedures.
- Poor photo baseline: hard to judge asymmetry later.
- Weak escalation plan: delayed response to red flags.
- Loose documentation: missing lot, site, or technique notes.
Clinic Operations: Sourcing, Documentation, and Stock Handling
Procurement teams often manage multiple HA options across providers and indications. Using a clear category structure helps. Many clinics start by browsing a hub such as Dermal Fillers, then narrow to Hyaluronic Acid Fillers to align products with internal protocols. The goal is consistency: fewer last-minute substitutions and fewer documentation gaps.
Inventory is sourced through vetted distributor networks for traceability.
Operationally, treat product selection and receiving as part of patient safety. Confirm packaging integrity, match lot numbers to invoices, and store per IFU. If your clinic supports multiple gel types within a line, keep naming conventions consistent in your EMR to avoid charting errors. If you reference specific items for staff education, do it neutrally and label-first, such as Stylage M Bi-Soft, Stylage L Bi-Soft With Lidocaine, or Stylage Lips Plus Bi-Soft. Keep training aligned to the specific presentation you stock.
If your sites standardize procurement centrally, document who can receive shipments and where they are stored on arrival. Some practices prefer US distribution for simpler internal logistics, but storage requirements still come from the IFU.
- Supplier verification: confirm licensure requirements and account access.
- Receiving checks: inspect seals and packaging condition.
- Traceability: record lot and expiry in inventory.
- Storage log: follow IFU temperature and light guidance.
- Chart integration: map product names to EMR templates.
- Adverse event file: keep protocols and contact lists current.
- Photo standards: consistent consent and image labeling.
Comparing Options: Interpreting “Vs” Searches and Reviews
Clinicians routinely see searches like Stylage filler vs Juvederm or Stylage filler vs Restylane. These comparisons are rarely about a single “best” product. They are about rheology, indication coverage, injector familiarity, and support systems for documentation and follow-up. If your practice carries multiple brands, build a comparison framework that starts with approved indications and IFU constraints, then adds your internal training and complication-readiness requirements.
Also treat “reviews” carefully. Stylage filler reviews may reflect technique, patient selection, and photography more than formulation differences. Separate product feedback (handling, extrusion feel, integration) from outcome judgments that may be confounded by swelling or editing. For deeper brand-to-brand reading inside your training library, you can cross-reference Stylage Vs Juvederm and Restylane Vs Juvederm. For a broader overview of selection categories, see Types Of Dermal Fillers and Stylage Dermal Fillers Range.
| Decision Factor | What to Check | Why It Affects “Natural” Results |
|---|---|---|
| Indication and plane | IFU, training, clinic protocol | Mismatch increases irregularity and dissatisfaction risk |
| Gel behavior | Elasticity/cohesivity descriptions and injector experience | Controls lift, spread, and integration in motion areas |
| Additives | Lidocaine presence and other excipients | May affect comfort and post-procedure expectations |
| Documentation | Lot/expiry capture, consent language, photo standards | Supports consistent follow-up and adverse event review |
| Clinic readiness | Escalation pathways and complication protocols | Faster recognition reduces harm if complications occur |
Brand documentation can support authenticity checks during receiving.
Authoritative Sources
- For an overview of filler risks and adverse events, see FDA dermal fillers safety information.
- For patient-facing counseling themes clinics often adapt, see American Academy of Dermatology dermal filler overview.
Natural-looking outcomes come from repeatable processes. Use label-first selection, standardized assessment, and strong documentation. When you evaluate a new line, focus on training alignment and complication readiness. For continued reading, you may also review Facial Volume Restoration within your staff education library.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.