Clinic teams are seeing steady demand for hyalgan knee injections within nonsurgical knee osteoarthritis pathways. As imaging becomes routine, expectations for placement accuracy and clean documentation rise. Robotics and navigation tools are also entering the conversation, with a focus on repeatable joint access.
This briefing is written for licensed healthcare providers and procurement teams. It stays high level and operational. It also flags where the package insert, payer policies, and local scope rules should lead decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Use label-first standards for series scheduling and documentation.
- Explain that this is viscosupplementation, not a steroid injection.
- Match technique choice to anatomy, staff training, and imaging access.
- Build lot traceability into receiving and procedure note templates.
Where Hyalgan Knee Injections Fit in Knee OA Care
Viscosupplementation (hyaluronic acid joint-fluid supplementation) is used in some practices for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. It is typically positioned after foundational nonpharmacologic measures and when analgesics or other conservative options do not meet goals. Your protocol should reflect current guidelines, patient selection standards, and payer requirements, which can vary by plan and setting.
Operationally, this therapy sits at the intersection of clinic workflow and procedure quality. Patient selection affects scheduling, inventory management, and follow-up touchpoints. Documentation needs usually include a clear diagnosis, prior conservative measures, informed consent elements, and a defensible rationale for the chosen product and approach. If you want a deeper operational discussion on candidacy, see Optimal Patient Selection and the broader overview in Types Of Gel Injections.
Many clinics also track whether a case is primarily pain-focused, function-focused, or activity-focused. That framing helps align expectations for “how long it takes,” what “working” means, and how follow-up calls are structured.
What Hyalgan Is and How It Works
Hyalgan is a hyaluronic acid product administered intra-articularly (within the joint). At a high level, hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring component of synovial fluid. In osteoarthritis, synovial fluid properties and joint homeostasis may change. Viscosupplementation aims to improve joint lubrication and mechanical cushioning, and may influence local inflammatory signaling. The mechanism is often described in functional terms rather than a single receptor effect.
For clinics, “what it is made from” matters for counseling and charting, especially with allergy histories and patient concerns. Hyaluronic acid products can be derived from avian (rooster comb) sources or produced by bacterial fermentation, depending on the formulation and manufacturer. Confirm the source, excipients, and warnings in the official labeling and your supplier documentation. For background reading that supports staff education, review Hyalgan And Hyaluronic Acid and Rooster Comb Injections.
Is it a steroid?
“Is hyalgan injection a steroid” is a common question at intake and check-in. It is not a corticosteroid (anti-inflammatory steroid). That distinction can influence patient expectations, post-procedure instructions, and how you document prior injections. It also affects how you discuss onset and duration, since clinics often see different timelines and response patterns between hyaluronic acid injections and steroid injections. Keep the language simple in consent discussions: “gel injection” is a useful plain-language synonym, while “intra-articular hyaluronic acid” is the clinical description.
Trust cue: Access is typically limited to licensed clinics and credentialed healthcare teams.
Series, Timing, and Expectations for Relief
Workflow planning starts with understanding that many hyaluronic acid products are used as a series rather than a one-time event. The hyalgan injection series, hyalgan injection frequency, and hyalgan injection protocol are label- and policy-dependent, and they are not interchangeable across brands. Avoid building a “one template fits all” series cadence. Instead, store product-specific series rules in your SOPs and inside scheduling notes, and reference the package insert for hyalgan injection dose and visit spacing.
Patients also ask how long does it take for hyalgan injections to work. In practice, onset can be variable. Some report improvement earlier, while others notice changes after subsequent visits. Your team can normalize that variability without promising timelines. It also helps to define what you track: pain scores, function scales, rescue medication use, or activity tolerance. If you coordinate rehab, align expectations with your physical therapy partners and consider the broader plan described in Combination Therapy With Physical Therapy.
Post-procedure activity questions come up daily, including exercise after hyalgan injection. Policies vary by clinic and by patient factors. Many sites provide a short, standardized activity handout that avoids over-specific claims and points patients back to clinician instructions. If your practice offers multiple nonsurgical options, keep a simple “pathways” handout so staff can describe where gel injections fit among alternatives; Non-Surgical Alternatives can help structure those conversations.
How to compare viscosupplements and steroid injections (clinic view)
Comparisons like hyalgan injection vs cortisone and brand-to-brand questions are best handled with a consistent framework. Keep the conversation focused on fit, constraints, and documentation rather than “best.” In operational terms, consider: labeled series structure, prior authorization needs, needle and volume logistics, and follow-up cadence. Also note whether your clinicians prefer ultrasound support for complex anatomy, and whether your chart templates capture the needed details for audits and continuity.
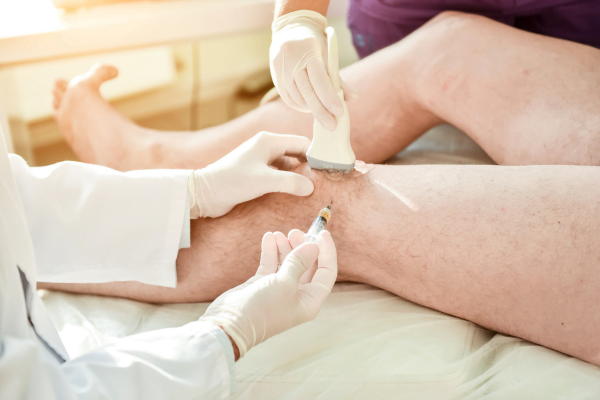
Technique Options: Landmark, Ultrasound, and Robotics
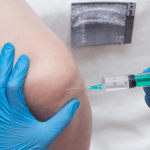
Technique selection should reflect training, patient anatomy, and the clinical setting. Landmark-guided injection can be appropriate in many routine cases. Ultrasound-guided hyalgan injection is often chosen when landmarks are difficult, effusion is present, or prior attempts were challenging. Some clinics also use fluoroscopic or other image-guided hyalgan injection approaches based on available equipment and expertise. Whatever method you use, standardize your documentation so it is clear whether the approach was landmark-based or image-guided, and what was visualized.
Why it matters: Standardized technique notes reduce rework when charts are reviewed later.
Image guidance and robotic assistance: what is changing
Robotic guidance for knee injections is an emerging concept rather than a universal standard. In broad terms, navigation or robot-assisted systems aim to improve consistency of needle trajectory and target access. They can also help with training by making steps more repeatable and measurable. That said, adoption depends on capital planning, credentialing, and local policy. If your organization is exploring robot-assisted hyalgan injections, involve compliance and risk teams early. Clarify how images are stored, who can operate the system, and how procedure notes should reference guidance tools without overstating accuracy or outcomes.
To support clinician education and reduce brand-driven debate, keep an internal comparison brief. The analysis in Comparing Hyaluronic Acid Injections and the focused discussion in Hyalgan Vs Synvisc can help structure staff training, even when your final choice is based on contracting and workflow fit.
Common pitfalls to address in SOPs
- Inconsistent approach notes that omit guidance method.
- Missing lot numbers in the procedure record.
- Unclear follow-up plan after the series ends.
- Staff overpromising onset or duration of relief.
Trust cue: Inventory is commonly sourced through screened, authorized distribution channels.
Safety, Contraindications, and Documentation
From a clinic perspective, safety work starts before the needle. Intake should capture key history elements and potential contraindications described in labeling, such as relevant allergies and local skin or joint concerns. During consent, use plain language for risks that matter operationally: pain flare, swelling, local reaction, and infection risk with any intra-articular procedure. Your template should also capture which knee was treated, the approach used, and any immediate reactions observed.
Staff often encounter online hyalgan injection reviews that mix personal experiences with unrelated conditions. Treat them as a prompt for education, not as clinical evidence. A simple script helps: “responses vary, and we follow labeling and your clinician’s plan.” If your practice uses individualized pathways (sports medicine, orthopedic, pain), align note templates with those pathways. For a structured approach, see Tailoring Injection Plans.
Common short-term reactions to track
When teams talk about hyalgan injection side effects, they often mean short-term local symptoms. Track post-procedure pain, warmth, swelling, and limitations that affect function or scheduling. Use consistent time stamps and escalation pathways in your nursing documentation. Also document counseling around red-flag symptoms, including fever, rapidly increasing pain, or inability to bear weight. Those elements support continuity and help your clinicians triage follow-up calls efficiently.
For internal quality review, it helps to monitor hyalgan injection effectiveness in a standardized way, even if you do not publish outcomes. Choose one or two simple measures and keep the capture burden low. This supports realistic conversations about hyalgan injection duration of relief without making promises, and it reduces variability between providers.
Operations Checklist for Procurement and Handling
Procurement for injectables is a compliance task as much as a supply task. Start by confirming who is authorized to request and receive products, how items are reconciled against invoices, and where lot and expiration details are recorded. If your clinic supports multiple service lines, align practices across teams that handle injectables, including those used outside orthopedics. Some organizations maintain shared receiving standards that also cover categories like Dermal Fillers, because traceability expectations are similar.
For clinics relying on US distribution, receiving logs should capture any exceptions the same day. Do not assume storage requirements are identical across brands or presentations. Follow the package insert and supplier documentation for storage conditions, light exposure, and handling limits. Build a “do not use if” checklist into receiving to reduce downstream waste and chart corrections.
- Licensure check: confirm facility credentials on file.
- Product match: verify NDC and description.
- Lot capture: record lot and expiration.
- Storage check: follow labeled conditions exactly.
- Chain notes: document handoffs between staff.
- Procedure link: map lot to the encounter.
- Reconciliation: resolve discrepancies promptly.
Quick tip: Put lot/exp fields in both inventory and procedure templates.
Keep product references factual and non-promotional in internal materials. If your team needs examples for catalog mapping, you can reference listings such as Hyalgan English 1 Syringe alongside other hyaluronic acid options like Euflexxa Prefilled Syringes or Durolane 3 mL. When comparing schedules (for example, Hyalgan, Supartz, or VISCO-3), keep series planning tied to labeling and payer rules rather than assumptions.
Trust cue: Brand-name items are supplied with lot details for traceability.
Authoritative Sources
- AAOS knee osteoarthritis clinical practice guideline
- FDA Drugs@FDA labeling and approvals database
- American College of Rheumatology osteoarthritis guidance
Further reading for your team can include product-specific labeling, payer policies, and internal competency checklists for image-guided procedures.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.