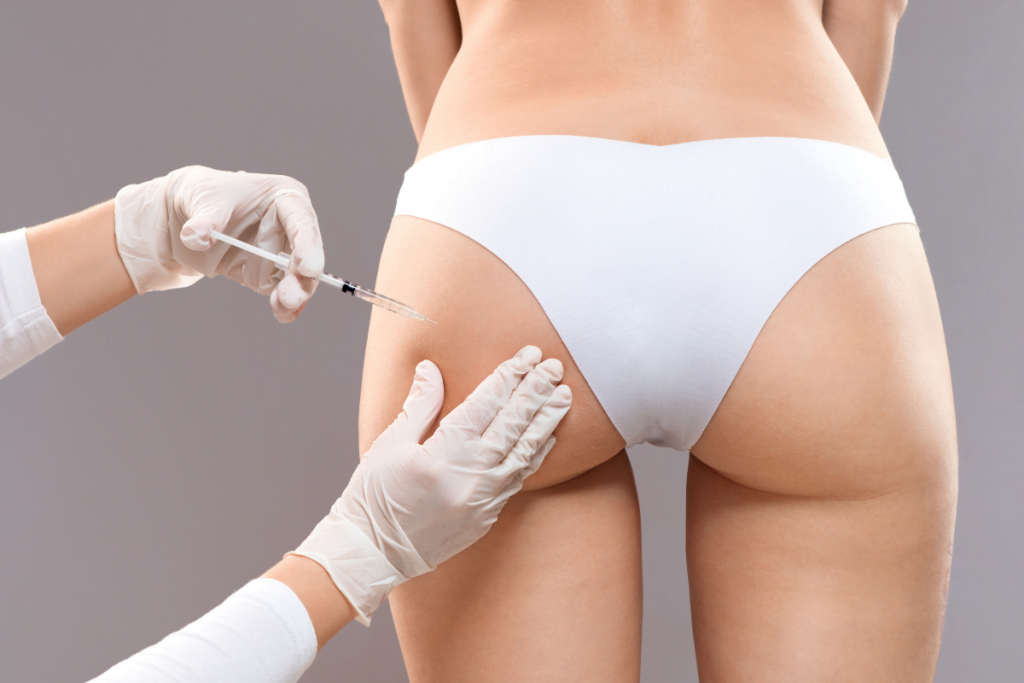
Interest in non-surgical gluteal augmentation has increased in many aesthetic practices. When clinics consider hyacorp filler for buttock contouring, the key questions are practical: who is an appropriate candidate, how to manage safety risk in a large treatment area, and what documentation supports traceability. This guide focuses on clinic-facing planning and compliance steps. It avoids dosing or patient-specific medical advice.
Because the buttocks involve larger volumes than most facial treatments, your risk controls need to scale. That includes consent language, photo documentation, product verification, and clear escalation pathways for post-procedure concerns. You will also want to align your team on what outcomes are realistic for soft-tissue fillers versus surgery.
Key Takeaways
- Screen carefully: confirm candidacy, contraindications, and realistic goals.
- Plan conservatively: staging, anatomy awareness, and documentation reduce avoidable risk.
- Standardize aftercare: written guidance and follow-up pathways support safer recovery.
- Protect traceability: lot tracking, chain-of-custody, and supplier vetting matter.
Supply is limited to licensed healthcare practices and professional use.
Where hyacorp filler Fits in Gluteal Contouring
Hyaluronic acid (HA) gels can be used for soft-tissue volume and contouring. In the buttocks, clinics often position HA treatment as an option for patients seeking modest shape changes without surgery. It is not the same goal as fat transfer (BBL) or implants. The clinical conversation is usually about contour refinement, symmetry, and targeted projection rather than large size changes.
Buttock anatomy makes this area operationally different from many injection sites. The region contains large muscle groups, variable subcutaneous fat, and important neurovascular structures. That translates into a stronger emphasis on anatomical knowledge, consistent aseptic technique, and a clear plan for recognizing and responding to complications.
What “Non-Surgical Augmentation” Means Operationally
In clinic operations, “non-surgical” should not mean “low effort” or “minimal risk.” It means the care pathway stays within an outpatient injectable workflow. You still need a structured consultation, informed consent, and robust documentation. For many practices, it also means coordinating staffing and room time differently than for facial filler visits. Large-area treatments can require more setup, more product handling steps, and more time for post-treatment monitoring. If your team already follows a body-contouring protocol, start by mapping how gluteal cases differ.
For background on HA body contouring concepts, see Hyacorp Body Contouring.
Formulation and Material Basics for Body HA
Not all HA gels behave the same. Product design choices influence how a gel integrates into tissue and how it handles compression and shear. In practice, clinicians and procurement teams often discuss “rheology” (how a material flows and resists deformation) when deciding whether a gel is intended for face, lips, or body areas. These properties may influence palpability, spread, and the clinician’s ability to sculpt.
When reviewing hyacorp filler as part of your injectable menu, look at the product’s intended use in its instructions for use (IFU), including any body-specific indications in your jurisdiction. Some product families include separate formulations marketed for different tissue needs, such as Hyacorp MLF2 and Hyacorp MLF1. Your clinical lead should match formulation selection to goals and anatomy, and your operations team should ensure labeling and lot details are captured consistently.
Rheology Terms Clinics Actually Use
Teams often translate technical rheology into practical language. “Lift” or “support” usually refers to how well a gel resists deformation under load. “Spread” relates to how easily the material distributes across a plane. “Cohesivity” describes how well it stays together instead of fragmenting. These terms can help align expectations during case planning and reduce mismatches between what a patient requests and what a gel is designed to do. If you document product selection rationale, keep it objective and tied to the IFU and your protocol.
Quick tip: Keep the IFU accessible in-room for reference and documentation.
Safety, Candidacy, and Contraindications
Large-area filler work requires a conservative candidacy screen. Your intake should separate cosmetic goals from functional complaints, and confirm the patient can follow aftercare guidance. It also helps to review prior procedures in the gluteal region, including surgery, implants, fat transfer, prior injectables, and any history of significant scarring or wound issues. Patients may describe prior products imprecisely, so documentation review matters.
When patients ask “hyacorp filler for buttocks is it safe,” a clinic-appropriate answer is that safety depends on patient selection, anatomy-aware technique, sterile handling, and timely response to complications. Every injectable carries risk. Common short-term effects can include swelling and bruising. More serious complications are uncommon but can be significant, including infection, vascular compromise, and tissue injury. Your protocols should outline contraindications, red flags, and an escalation plan consistent with local regulations and your medical director’s guidance.
Inventory focuses on brand-name products with authenticity as a priority.
Also plan for reversibility discussions. HA is often described as “dissolvable” because hyaluronidase can break down hyaluronic acid. In large-volume body cases, reversibility can be more complex than in small facial corrections. Document the counseling clearly, including uncertainties and limitations, and follow your standard risk consent framework.
Technique Planning and Comparing Modalities
Buttock filler work is primarily about risk-managed planning. The clinician should decide on plane, access points, and instrumentation (needle vs cannula) based on training, anatomy, and protocol. Ultrasound guidance may be considered in some practices to support safer placement and to evaluate unusual findings. Whatever technique is used, operational consistency matters: aseptic prep, standardized timeouts, and clear documentation of product, lot, and placement plan.
Volume planning is another operational variable. Many clinics prefer staged sessions for larger contour goals to reduce swelling-related distortion and to reassess symmetry. Avoid treating “volume per session” as a marketing number. Treat it as a clinical decision that is documented and revisited over time.
How to Compare HA Fillers vs Biostimulators
Patients may request comparisons such as “hyaluronic acid buttock injections vs sculptra.” Keep comparisons neutral and tied to material properties and workflow. HA fillers are gels that provide immediate volume at placement and are often considered adjustable. Poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA, commonly discussed under brand names) is a biostimulator intended to trigger gradual collagen response, which changes timelines and follow-up expectations. Calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHA) products are different again and may have distinct handling and imaging considerations. Regulatory status and indications vary widely by country and by product, so verify the IFU for your market before adopting any protocol.
| Decision factor | HA gel fillers (body use) | Biostimulators (e.g., PLLA) |
|---|---|---|
| Onset pattern | Often immediate volume at placement | More gradual tissue response over time |
| Reversibility | May be enzymatically degradable (hyaluronidase), with limits | Not typically reversed in the same way |
| Documentation needs | Lot tracking, injection map, and aftercare instructions | Lot tracking plus longer outcome-tracking cadence |
| Regulatory considerations | Indications vary by product and jurisdiction | Indications vary; confirm local authorization |
For broader modality context, you can review Body Contouring Treatments and Non-Invasive Fat Removal.
- Pitfall: vague documentation of injection planes and sites.
- Pitfall: skipping baseline photos due to time pressure.
- Pitfall: underestimating swelling-related asymmetry early on.
- Pitfall: inconsistent post-procedure contact instructions.
Some clinics also carry alternative injectables for other indications. When you reference comparators, keep it factual and product-specific. Examples include Radiesse and Ultracol, but product use depends on local labeling and clinician judgment.
Aftercare, Recovery, and Documentation
Aftercare for buttock filler should be written, standardized, and easy to follow. Many practices include activity modification guidance, hygiene reminders, and instructions on what to expect in the first days. Recovery time can vary with treatment extent, patient factors, and technique. Because the area is weight-bearing and prone to friction, comfort and swelling management plans should be practical.
When you use hyacorp filler in this region, anticipate common short-term effects such as swelling and bruising, and ensure your team can explain expected variability without overpromising. Also document what your clinic told the patient about “before and after” expectations. High-quality baseline photography (consistent angles, lighting, and stance) helps interpretation. It also protects the clinic if early swelling creates a temporary change that patients misread as a final result.
Why it matters: Clear aftercare reduces avoidable calls and missed warning signs.
Build your follow-up process around risk signals, not routine reassurance. Staff should know how to route concerns, including signs of infection, unusual pain, skin color changes, fever, or rapidly progressing swelling. Keep language general in public-facing materials, but keep your internal escalation criteria specific and documented. For a broader discussion of filler counseling and side effects across indications, see Dermal Fillers Overview.
Patient demographics can shape counseling needs. For example, men seeking body contouring may prioritize different proportions and may have different baseline tissue distribution. See Aesthetic Treatments For Men for related practice trends.
Clinic Operations Checklist: Sourcing to Records
From a procurement standpoint, hyacorp filler should be handled like any other implantable or injectable device: maintain traceability, verify supplier legitimacy, and store per labeled requirements. Build an audit-ready paper trail that connects the patient chart to product name, lot number, and expiration date. Policies vary by state and facility type, so align your workflow with your medical director and compliance lead.
Sourcing relies on screened distributors rather than open-market purchasing.
Clinic Workflow Snapshot
- Verify: confirm clinician licensure and facility scope.
- Document: capture indications, consent, photos, and treatment plan.
- Receive: inspect packaging integrity and expiration dates.
- Record: log lot numbers and assign to patient records.
- Store: follow labeled storage and inventory rotation.
- Use: maintain aseptic handling and standardized setup.
- Track: note any adverse events and internal quality reviews.
If you rely on US distribution, confirm how lot documentation is provided and retained. If products are shipped from the US, clarify chain-of-custody and receiving checks in advance.
When browsing related items for your formulary review, use category hubs as a starting point rather than a selection shortcut, such as the Uncategorized Category. Your final decision should be based on the IFU, staff training, and your clinic’s complication management readiness.
Authoritative Sources
Regulatory status for dermal fillers and body contouring products varies by jurisdiction. For any product you evaluate, verify local authorization, labeled indications, and required adverse event reporting pathways. Use primary sources for these checks, then align your clinic policies to your licensing board and facility requirements.
These references can support internal education and compliance reviews:
- FDA overview of dermal fillers and regulatory considerations
- European Commission information on CE marking for devices
- American Academy of Dermatology guidance on fillers
Further reading: review your local IFU, your adverse event procedure, and your documentation templates at least annually.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.